Understanding Thyroiditis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Thyroiditis is a medical condition characterized by the inflammation of the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism by producing hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). When the thyroid becomes inflamed, it can result in various health issues. This article will delve into the different types of thyroiditis, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, providing comprehensive information for those seeking to understand this condition better.
Types of Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis encompasses several different conditions, each with its own causes and characteristics. The main types include:
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
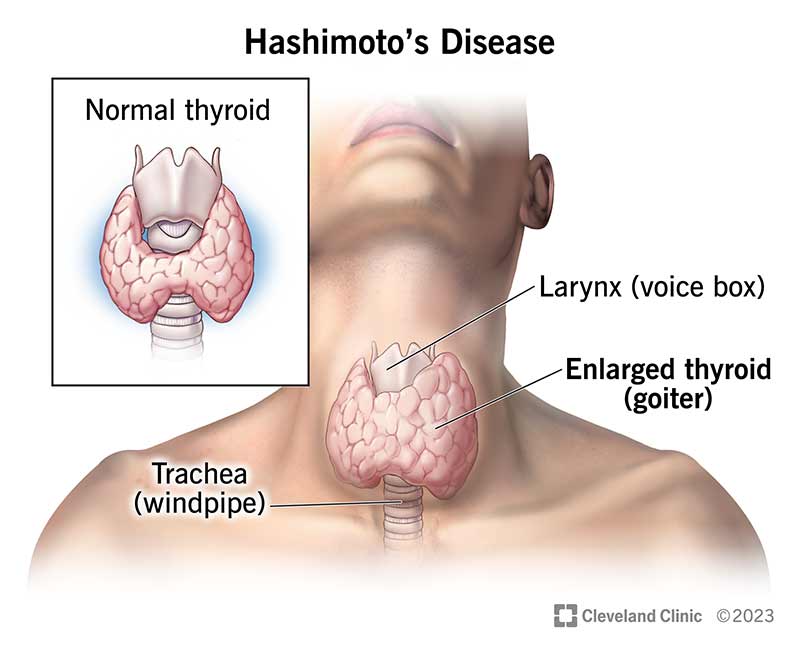
The immune system targets the thyroid gland in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, also referred to as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis. This type of thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid). It can lead to gradual thyroid gland failure, where the gland no longer produces sufficient hormones. - Subacute Thyroiditis
Subacute thyroiditis, also known as De Quervain’s thyroiditis, is often caused by a viral infection. It is characterized by a sudden onset of pain in the thyroid gland, which may radiate to the jaw or ears. This type of thyroiditis usually follows an upper respiratory tract infection. - Postpartum Thyroiditis
Postpartum thyroiditis occurs in some women after childbirth. It is an autoimmune condition and typically involves a phase of hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) followed by hypothyroidism. Most women eventually regain normal thyroid function, but some may develop permanent hypothyroidism. - Silent Thyroiditis
Silent thyroiditis, also known as painless thyroiditis, is another autoimmune condition that can occur spontaneously or be triggered by certain medications. It is characterized by a painless enlargement of the thyroid gland and can also involve phases of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. - Acute Thyroiditis
Acute thyroiditis, also known as suppurative thyroiditis, is a rare condition caused by a bacterial infection. It presents with severe pain, fever, and redness over the thyroid gland and requires immediate medical attention.
Causes of Thyroiditis
Depending on the kind, thyroiditis has different causes. However, some common factors include:
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, are a primary cause of thyroiditis. Conditions such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and postpartum thyroiditis fall into this category.
Infections
Viral infections can lead to subacute thyroiditis, while bacterial infections can cause acute thyroiditis. The inflammation results from the body’s immune response to these infections.
Medications
Certain medications, including lithium and interferons, can induce thyroiditis. These drugs may trigger an immune response or directly damage the thyroid gland.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy to the neck area can cause inflammation of the thyroid gland, leading to thyroiditis. This is often seen in patients undergoing treatment for cancers of the head and neck.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition plays a role in the development of autoimmune thyroiditis. A family history of thyroid or other autoimmune diseases increases the risk of developing conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Symptoms of Thyroiditis
The symptoms of thyroiditis depend on the type and the phase of the condition. Common symptoms include:
Hypothyroidism Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Hair loss
- Depression
- Muscle weakness
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
- Weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Tremors
- Heat intolerance
- Palpitations
- Increased sweating
- Insomnia
Specific Symptoms for Types of Thyroiditis
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Goiter (enlarged thyroid gland), feeling of fullness in the neck
- Subacute Thyroiditis: Pain in the neck, jaw, or ears, fever, and tenderness over the thyroid gland
- Postpartum and Silent Thyroiditis: Mild symptoms similar to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism phases
- Acute Thyroiditis: Severe neck pain, fever, redness, and swelling over the thyroid gland
Diagnosis of Thyroiditis
Diagnosing thyroiditis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
Medical History and Physical Examination
A detailed medical history and physical examination help in identifying symptoms and signs of thyroid inflammation. The doctor may palpate the thyroid gland to check for enlargement, tenderness, or nodules.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are crucial in diagnosing thyroiditis. These tests measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and thyroid antibodies. Abnormal levels can indicate whether the thyroid is underactive or overactive and suggest an autoimmune cause.
Imaging Studies
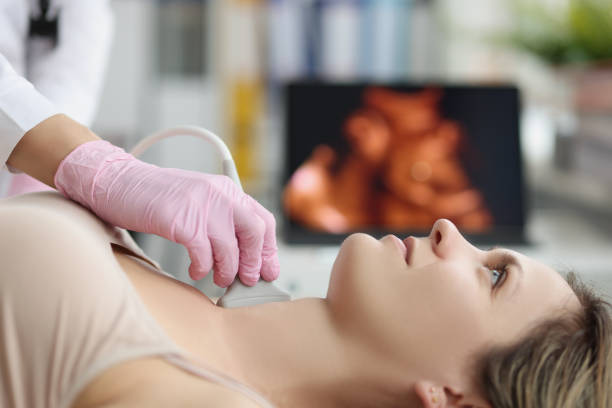
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland can help assess the size, structure, and presence of nodules or inflammation. In some cases, a radioactive iodine uptake test may be performed to evaluate thyroid function and differentiate between different types of thyroiditis.
Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
In certain cases, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy may be necessary to obtain a tissue sample from the thyroid gland. This helps in ruling out other thyroid conditions, such as cancer, and confirms the diagnosis of thyroiditis.
Treatment Options for Thyroiditis
The treatment for thyroiditis depends on the type, severity, and phase of the condition. Here are the common approaches:
Medications
- Hypothyroidism: Synthetic thyroid hormone replacement therapy (levothyroxine) is prescribed to normalize thyroid hormone levels.
- Hyperthyroidism: Beta-blockers may be used to control symptoms like palpitations and tremors. Anti-thyroid medications may be necessary in some cases.
Pain Management
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or aspirin can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation in subacute and acute thyroiditis.
Antibiotics
For acute thyroiditis caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics are required to treat the underlying infection.
Monitoring
In cases of silent and postpartum thyroiditis, regular monitoring of thyroid function is essential. Most patients recover without specific treatment, but some may need temporary thyroid hormone replacement.
Surgery
Surgery is rarely required but may be considered in cases of severe, refractory thyroiditis or if there is suspicion of thyroid cancer.
Conclusion
Thyroiditis is a diverse group of conditions that cause inflammation of the thyroid gland. Understanding the different types, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. If you suspect you have thyroiditis or are experiencing symptoms, it is essential to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and prevent long-term complications, ensuring better thyroid health and overall well-being.