Understanding Thyroid Nodules: What You Need To Know
Millions of people throughout the world suffer from thyroid nodules, a common thyroid condition. While most thyroid nodules are benign and harmless, understanding their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for proper management and peace of mind. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of thyroid nodules, shedding light on what you need to know to navigate this condition effectively.
What are Thyroid Nodules?
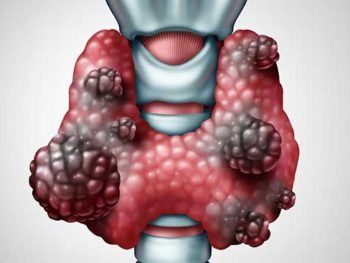
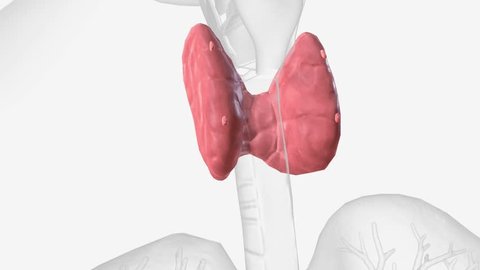
Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths or lumps that form within the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck. These nodules can vary in size, ranging from small, pea-sized nodules to larger growths that are visible or palpable. While the majority of thyroid nodules are noncancerous (benign), a small percentage may harbor malignancy (cancerous).
Causes of Thyroid Nodules
The exact cause of thyroid nodules remains unclear, but several factors may contribute to their development:
- Iodine Deficiency: In regions with iodine deficiency, the thyroid gland may develop nodules as it tries to compensate for inadequate iodine intake.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland, known as thyroiditis, can lead to the formation of nodules.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer may increase the risk of developing nodules.
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to radiation, particularly during childhood or adolescence, has been associated with an increased risk of thyroid nodules.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Imbalances in thyroid hormones, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, may contribute to the formation of nodules.
Symptoms of Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules often do not cause any symptoms and are incidentally discovered during routine physical exams or imaging studies. However, some individuals may experience symptoms such as:
- Swelling or lump in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing, particularly with larger nodules
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Thyroid enlargement (goiter)
- Pain or discomfort in the neck
It’s important to note that the presence of symptoms does not necessarily indicate malignancy, as benign nodules can also cause similar symptoms.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules
Diagnosing thyroid nodules typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
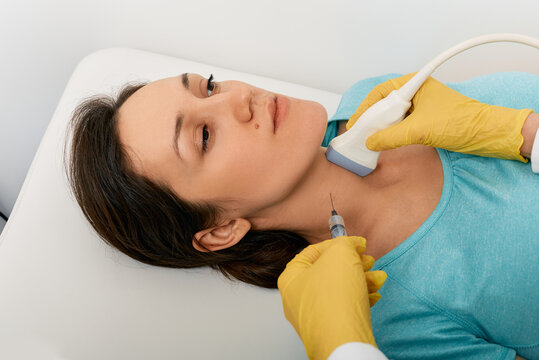
- Thyroid Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging is commonly used to evaluate thyroid nodules, providing detailed information about their size, shape, and characteristics.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: If a nodule is suspicious or has concerning features, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy may be performed to collect cells for examination under a microscope. This helps determine whether the nodule is benign or malignant.
- Thyroid Function Tests: Blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4) can help assess thyroid function and detect hormonal imbalances.
- Imaging Studies: In some cases, additional imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI scans may be recommended to further evaluate the thyroid gland and surrounding structures.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Nodules
The management of thyroid nodules depends on various factors, including the size, characteristics, and presence of symptoms. Treatment options may include:
- Observation: Small, asymptomatic nodules may simply be monitored over time without intervention, especially if they are determined to be benign.
- Thyroid Hormone Therapy: In some cases, thyroid hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed to help shrink nodules or manage underlying thyroid conditions.
- Thyroid Nodule Ablation: Ablative techniques such as ethanol ablation or radiofrequency ablation may be used to shrink or destroy thyroid nodules, particularly for those who are not candidates for surgery.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of thyroid nodules (thyroidectomy) may be recommended for nodules that are suspicious for cancer, causing significant symptoms, or enlarging over time.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: Radioactive iodine may be used to treat hyperfunctioning (hot) nodules or thyroid cancer.
Living with Thyroid Nodules
Living with thyroid nodules involves regular monitoring, adherence to treatment plans, and proactive communication with healthcare providers. Individuals with thyroid nodules should:
- Attend regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor nodule size and function.
- Take prescribed medications as directed, if applicable.
- Keep up a healthy lifestyle that includes frequent exercise and a balanced food.
- Educate themselves about thyroid nodules and stay informed about new developments in treatment and management options.
Conclusion
One common thyroid condition that needs to be carefully evaluated and managed is thyroid nodules. While most nodules are benign and do not cause symptoms, prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for ensuring optimal outcomes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for thyroid nodules, individuals can take proactive steps to address this condition effectively and maintain their overall health and well-being.
If you have concerns about thyroid nodules or are experiencing symptoms associated with thyroid disorders, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for evaluation and personalized management recommendations. With proper care and guidance, individuals with thyroid nodules can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.