Treatment for Hyperthyroidism
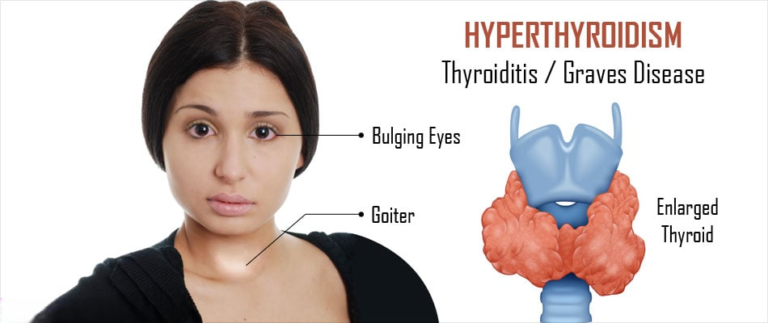
Hyperthyroidism, a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, requires careful management to alleviate symptoms and prevent potential complications. The treatment approach for hyperthyroidism has evolved over the years, offering patients various options tailored to their specific needs. In this article, we will explore the diverse methods of treating hyperthyroidism, from traditional approaches to innovative therapies.
Traditional Treatment Options
Antithyroid Medications:
The cornerstone of hyperthyroidism treatment often involves antithyroid drugs, such as methimazole and propylthiouracil. These medications work by inhibiting the production of thyroid hormones. While effective, they may require long-term use and periodic monitoring to manage potential side effects.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy:
Another common treatment is radioactive iodine therapy, which involves the oral administration of radioactive iodine. The radioactive substance selectively targets and destroys overactive thyroid cells. This treatment is effective, but it may lead to hypothyroidism over time, necessitating thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Thyroidectomy:
Surgical intervention, known as thyroidectomy, involves the partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland. This option is considered when other treatments are unsuitable or when there’s a need for swift resolution, such as in severe cases or when there’s resistance to antithyroid medications.
Emerging and Innovative Treatments
Monoclonal Antibodies:
Recent advances in biotechnology have led to the development of monoclonal antibodies targeting specific pathways involved in hyperthyroidism. These antibodies, such as rituximab, show promise in modulating the immune response responsible for the overproduction of thyroid hormones.
Small Molecule Inhibitors:
Researchers are exploring small molecule inhibitors that target key enzymes involved in thyroid hormone synthesis. These inhibitors, still in the experimental stage, offer the potential for more precise and targeted therapy with fewer side effects.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT):
PRRT, traditionally used in the treatment of certain cancers, is being investigated for its potential in hyperthyroidism. This therapy involves the administration of radioactive peptides that bind to receptors on overactive thyroid cells, delivering targeted radiation to reduce hormone production.
Personalized Approaches
Genetic and Molecular Profiling:
Advances in genetic and molecular testing allow for a more personalized approach to hyperthyroidism treatment. Identifying specific genetic markers associated with the condition enables healthcare providers to tailor treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup.
Precision Medicine:
The concept of precision medicine is gaining traction in hyperthyroidism management. By considering factors such as genetic predisposition, lifestyle, and environmental influences, healthcare providers can optimize treatment plans for better outcomes.
Comprehensive Care and Patient Education
Integrated Care Models:
Holistic approaches to hyperthyroidism treatment involve integrating medical, nutritional, and psychological support. Collaborative care models ensure that patients receive comprehensive treatment, addressing not only the physiological aspects of the condition but also its impact on mental and emotional well-being.
Patient Education and Empowerment:
Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition is crucial. Education on medication management, lifestyle modifications, and the importance of regular follow-ups promotes active patient participation in their treatment plan.
In conclusion, the landscape of hyperthyroidism treatment is evolving, offering a range of options from traditional methods to cutting-edge therapies. Advances in research, personalized medicine, and comprehensive care models aim to enhance treatment efficacy, minimize side effects, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals managing hyperthyroidism. As the field continues to progress, patients and healthcare providers alike can look forward to a future where hyperthyroidism is managed with greater precision and effectiveness.
For further queries, please visit https://drtanejathyroidclinic.com/