Thyroiditis Ultrasound Radiology
Thyroiditis, characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland, is a condition that often necessitates thorough diagnostic evaluation. Ultrasound radiology emerges as a crucial tool in the diagnosis and monitoring of thyroiditis, providing detailed images that aid healthcare professionals in understanding the extent of inflammation, identifying nodules, and guiding treatment decisions.
The Role of Ultrasound in Thyroiditis Diagnosis
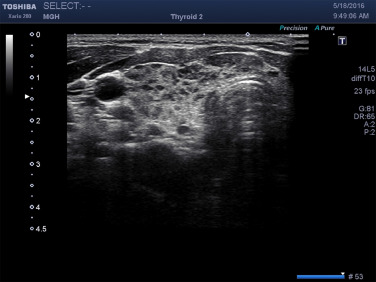
Ultrasound imaging offers a non-invasive and highly informative method for visualizing the thyroid gland. When it comes to thyroiditis, ultrasound plays a pivotal role in confirming the diagnosis and assessing the severity of inflammation. The distinctive patterns of inflammation, such as hypoechoic regions and irregularities in thyroid tissue, are readily detectable through ultrasound, aiding radiologists in distinguishing between different types of thyroiditis.
Differentiating Types of Thyroiditis through Ultrasound Features
Each type of thyroiditis presents unique ultrasound features. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, for instance, often exhibits a diffuse pattern of hypoechogenicity with a coarse and heterogeneous texture. On the other hand, subacute thyroiditis may show focal areas of hypoechogenicity with increased blood flow, reflecting the acute inflammatory process. By recognizing these distinctive ultrasound patterns, radiologists can contribute to a more accurate and timely diagnosis, facilitating the formulation of an appropriate treatment plan.
Nodule Identification and Risk Stratification
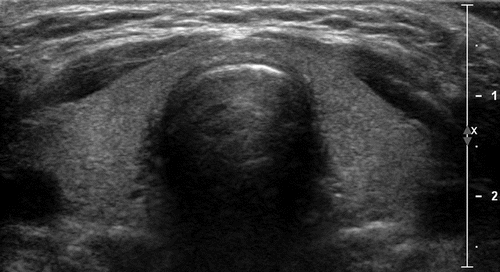
Thyroid nodules are a common finding in thyroid imaging, and their presence adds complexity to the diagnostic process. Ultrasound allows for the characterization of these nodules, helping to determine whether they are benign or potentially malignant. In the context of thyroiditis, the identification and evaluation of nodules become critical, as certain types of thyroiditis may increase the risk of developing thyroid nodules. Through ultrasound, radiologists can assess the size, shape, and vascularity of nodules, aiding in risk stratification and guiding decisions regarding further evaluation or intervention.
Monitoring Thyroiditis Progression and Treatment Response
Ultrasound radiology serves as a dynamic tool for monitoring the progression of thyroiditis and evaluating the response to treatment. Serial ultrasound examinations can track changes in thyroid size, echogenicity, and the presence of nodules over time. This longitudinal assessment is invaluable in guiding treatment adjustments and ensuring that interventions are effective in mitigating inflammation and preserving thyroid function.
Challenges and Considerations in Thyroiditis Ultrasound Imaging
While ultrasound is highly valuable in thyroiditis diagnosis and management, it is not without challenges. The interpretation of ultrasound images requires expertise, and variations in operator skills can impact the accuracy of the diagnosis. Additionally, ultrasound may not provide a definitive diagnosis in some cases, necessitating the use of complementary diagnostic modalities.
Enhancing Thyroiditis Management through Ultrasound Radiology
Thyroiditis ultrasound radiology plays a pivotal role in the comprehensive evaluation and management of thyroid inflammation. From confirming the diagnosis to differentiating between types of thyroiditis and monitoring treatment response, ultrasound imaging offers valuable insights. As technology advances and imaging techniques become more sophisticated, the role of ultrasound in thyroiditis diagnosis and management continues to evolve, contributing to more personalized and effective patient care.
For further queries, please visit https://drtanejathyroidclinic.com/