Targeted Therapies: Breakthroughs In Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, affects millions of people worldwide. Traditionally, its treatment has centered around medications to regulate hormone levels or radioactive iodine therapy. However, recent breakthroughs in medical science have led to the development of targeted therapies, offering new hope for those struggling with this challenging condition. In this article, we will explore the latest advancements in targeted therapies for hyperthyroidism and their potential implications for patients.
Understanding Hyperthyroidism
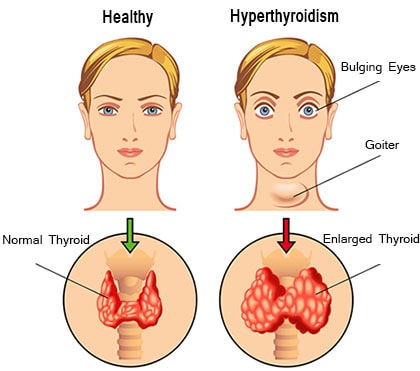
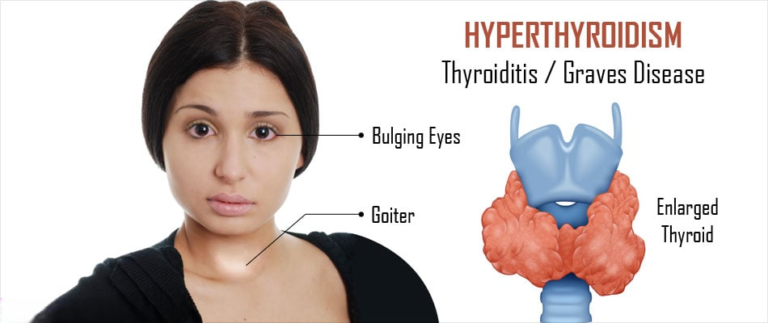
Before delving into targeted therapies, it’s essential to understand the mechanisms underlying hyperthyroidism. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones (thyroxine or T4 and triiodothyronine or T3) that regulate metabolism. In hyperthyroidism, the thyroid gland becomes overactive, leading to an excess production of these hormones. This can result in a myriad of symptoms, including weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, fatigue, and heat intolerance.
Traditional Treatment Approaches
Historically, treatment options for hyperthyroidism have primarily focused on reducing thyroid hormone levels. Antithyroid medications such as methimazole and propylthiouracil work by inhibiting the production of thyroid hormones. Another common approach is radioactive iodine therapy, where radioactive iodine is administered orally to destroy thyroid cells, thereby reducing hormone production. In severe cases, surgical removal of the thyroid gland may be necessary.
Challenges with Traditional Treatments
While these conventional treatments can effectively manage hyperthyroidism in many cases, they are not without limitations. Antithyroid medications may cause adverse effects such as skin rash, liver toxicity, or agranulocytosis, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by a severe decrease in white blood cell count. Radioactive iodine therapy carries the risk of permanent hypothyroidism, requiring lifelong hormone replacement therapy. Additionally, some patients may experience a recurrence of hyperthyroidism after initial treatment, necessitating further interventions.
Enter Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies represent a paradigm shift in the treatment of hyperthyroidism, offering more precise and tailored approaches to managing the condition. Unlike traditional treatments, which broadly suppress thyroid function, targeted therapies aim to interfere with specific molecular pathways involved in the development and progression of hyperthyroidism.
One promising avenue of targeted therapy involves monoclonal antibodies that selectively target receptors on thyroid cells. For instance, monoclonal antibodies that block the action of the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor have shown efficacy in reducing thyroid hormone levels in patients with Graves’ disease, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
Another innovative approach is the use of small molecule inhibitors that target enzymes involved in thyroid hormone synthesis. For example, drugs that inhibit the activity of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) receptors or sodium-iodide symporters (NIS) could potentially offer new options for controlling thyroid hormone production.
Furthermore, advancements in understanding the genetic basis of hyperthyroidism have paved the way for personalized therapies based on individual genetic profiles. By identifying genetic mutations associated with hyperthyroidism, researchers can develop targeted treatments that address the underlying molecular abnormalities driving the disease.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Therapies
Numerous clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of targeted therapies for hyperthyroidism. These trials are exploring a variety of approaches, including novel drug compounds, gene therapies, and immunomodulatory agents. While many of these treatments are still in the experimental stages, preliminary results are promising, offering hope for more effective and tolerable therapies in the future.
For example, recent studies have investigated the use of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, which block signaling pathways involved in thyroid hormone production. Initial findings suggest that JAK inhibitors may offer a promising therapeutic option for patients with refractory hyperthyroidism or those who cannot tolerate traditional treatments.
Another area of active research is the development of vaccines targeting the TSH receptor or other antigens implicated in autoimmune thyroid disorders. Vaccines could potentially provide long-term remission or even cure for patients with Graves’ disease or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, autoimmune conditions that can lead to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, respectively.
Implications for Patients
The emergence of targeted therapies holds significant implications for patients with hyperthyroidism. These therapies offer the potential for more tailored and effective treatment approaches, with fewer side effects compared to conventional treatments. Additionally, targeted therapies may provide alternatives for patients who have failed or cannot tolerate traditional treatments, expanding the therapeutic options available.
However, it’s important to note that targeted therapies are still in the early stages of development, and more research is needed to fully understand their safety, efficacy, and long-term outcomes. Furthermore, access to these therapies may be limited initially, as they undergo regulatory approval and become more widely available.
Conclusion
In conclusion, targeted therapies represent a promising frontier in the management of hyperthyroidism, offering new avenues for treatment that are more precise, effective, and tailored to individual patients. While still in the early stages of development, these therapies hold the potential to revolutionize the standard of care for hyperthyroidism and improve outcomes for patients worldwide. Continued research and clinical trials are essential to further elucidate the role of targeted therapies in hyperthyroidism and bring these innovative treatments to fruition.