Simple Goitre: Understanding The Basics
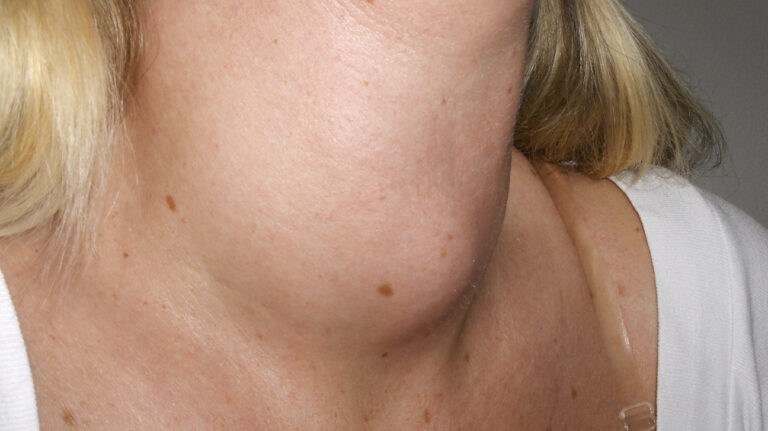
A goitre is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck just below the Adam’s apple. While goitre can be associated with various thyroid conditions, a “simple goitre” refers to an enlargement of the thyroid gland that isn’t related to inflammation, cancer, or hypothyroidism/hyperthyroidism. Understanding simple goitre is crucial for early detection and effective management.
What is Simple Goitre?
A simple goitre is a non-toxic enlargement of the thyroid gland that often results from iodine deficiency or other environmental factors. Unlike other thyroid conditions, simple goitre typically does not affect thyroid hormone levels significantly. The thyroid gland may become uniformly enlarged or develop nodules (lumps).
Types of Simple Goitre
- Diffuse Goitre: The thyroid gland enlarges uniformly.
- Nodular Goitre: The gland develops one or more nodules, which can be felt upon examination.
Causes and Risk Factors
Iodine Deficiency
Iodine is a critical component of thyroid hormones. When iodine intake is insufficient, the thyroid gland enlarges to trap more iodine from the bloodstream, leading to goitre. Iodine deficiency is the leading cause of simple goitre globally.
Environmental Factors
Goitrogens: Certain foods and environmental substances can interfere with thyroid function, such as cassava, millet, and vegetables from the cruciferous family (e.g., cabbage, broccoli).
Medications: Some drugs, like lithium and amiodarone, can affect thyroid function and contribute to goitre development.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can increase the demand for thyroid hormones, potentially leading to goitre.
Genetic Predisposition
A family history of thyroid disorders can increase the likelihood of developing a goitre.
Smoking
Thiocyanates in tobacco smoke can interfere with iodine uptake by the thyroid gland, contributing to goitre formation.
Symptoms of Simple Goitre
Simple goitre often presents with a visible swelling at the base of the neck. Other symptoms may include:
- A tight feeling in the throat
- Coughing or hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty breathing (in severe cases)
Despite these symptoms, many individuals with simple goitre do not experience significant discomfort and may only discover the condition during a routine physical examination.
Diagnosis
Physical Examination
A physical exam involves the doctor palpating (feeling) your neck to check for thyroid enlargement and nodules.
Blood Tests
Blood tests measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to ensure thyroid function is normal.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging helps assess the size and texture of the thyroid gland and identify the presence of nodules.
Thyroid Scan
A thyroid scan involves swallowing or injecting a small amount of radioactive iodine, which collects in the thyroid gland. The scan provides detailed images of the thyroid’s structure and function.
Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy
In cases where nodules are present, a fine needle aspiration biopsy may be performed to rule out malignancy.
Treatment Options
Observation
If the goitre is small and not causing symptoms, the doctor may recommend a “watchful waiting” approach, with regular check-ups to monitor the condition.
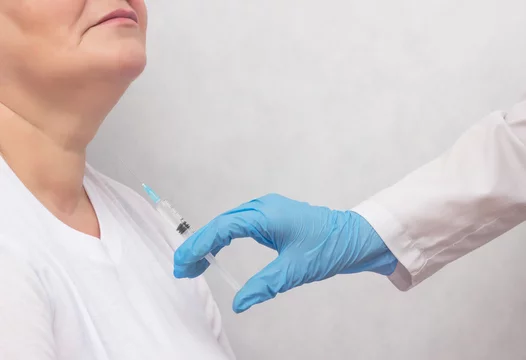
Iodine Supplementation
In cases of iodine deficiency, iodine supplementation can reduce the size of the goitre. This may involve dietary changes or iodine supplements.
Medications
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed to shrink the goitre, particularly if the patient has mild hypothyroidism.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
For larger goitres causing symptoms, radioactive iodine can be used to shrink the thyroid gland. This treatment is more commonly used in hyperthyroid conditions but can be effective for reducing the size of a goitre.
Surgery
In cases where the goitre is large, causes significant symptoms, or is cosmetically concerning, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be necessary.
Preventing Simple Goitre
Adequate Iodine Intake
Ensuring sufficient iodine intake through diet is the most effective way to prevent simple goitre. Iodized salt is a common and effective source of iodine. Foods rich in iodine include:
- Seafood (fish, shrimp)
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
- Eggs
- Iodine-fortified foods
Avoiding Goitrogens
Limiting foods high in goitrogens, such as certain raw cruciferous vegetables (e.g., cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower), can help prevent goitre, especially in individuals with low iodine intake. Cooking these vegetables reduces their goitrogenic effect.
Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups can help detect thyroid enlargement early, allowing for prompt intervention.
Living with Simple Goitre
For many individuals, living with a simple goitre involves regular monitoring and maintaining a balanced diet. Here are some tips for managing the condition:
- Follow Medical Advice: Adhere to the treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure your diet includes sufficient iodine and other essential nutrients.
- Monitor Symptoms: Make note of any changes in your symptoms and let your doctor know about them.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can exacerbate thyroid problems; quitting smoking can improve overall thyroid health.
Complications
While simple goitre is usually benign, complications can arise if left untreated:
- Compression Symptoms: A large goitre can compress the windpipe (trachea) and esophagus, causing difficulty breathing and swallowing.
- Hyperthyroidism: In rare cases, a simple goitre can lead to overproduction of thyroid hormones.
- Thyroid Cancer: Although rare, nodular goitres can occasionally harbor cancerous cells, underscoring the importance of proper evaluation.
Conclusion
Simple goitre is a common thyroid condition, primarily resulting from iodine deficiency. Understanding the basics of this condition, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, is essential for effective management. With adequate iodine intake and regular medical check-ups, simple goitre can often be managed successfully, ensuring a good quality of life for those affected.