Research Advances In Thyroiditis: Promising Therapies And Future Directions
Thyroiditis, an inflammation of the thyroid gland, encompasses a spectrum of disorders with varying causes, symptoms, and treatments. While traditional management strategies have focused on mitigating symptoms and addressing underlying causes, recent research has propelled the development of innovative therapies and provided insight into potential future directions in the treatment of thyroiditis. This article explores some of the promising advancements in thyroiditis research, including novel therapies and emerging trends that offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Understanding Thyroiditis
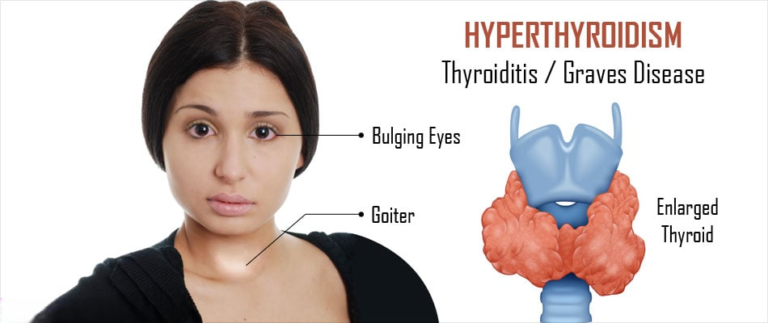
Thyroiditis refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck that plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and energy levels. The condition can manifest in several forms, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, a common autoimmune disorder characterized by the immune system attacking the thyroid tissue, and subacute thyroiditis, which typically follows a viral infection and leads to temporary inflammation and dysfunction of the gland.
Promising Therapies
- Immunomodulatory Agents: One of the most significant advancements in thyroiditis research involves the development of immunomodulatory therapies designed to target the underlying autoimmune mechanisms driving conditions such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Biologic agents, including monoclonal antibodies that block specific immune pathways, have shown promise in reducing inflammation and preserving thyroid function in clinical trials.
- Precision Medicine Approaches: The advent of precision medicine has revolutionized the management of thyroiditis by enabling personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual patients’ genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. Genetic profiling and biomarker analysis help identify patients who are most likely to benefit from specific therapies, minimizing trial and error in treatment selection.
- Regenerative Medicine: Regenerative therapies, such as stem cell transplantation and tissue engineering, offer potential avenues for restoring thyroid function in cases where glandular damage has occurred. Preclinical studies have demonstrated the ability of stem cells to differentiate into thyroid follicular cells and regenerate damaged tissue, raising hopes for regenerative approaches to thyroiditis treatment in the future.
- Targeted Drug Delivery Systems: Drug delivery systems utilizing nanoparticles and targeted drug delivery vehicles show promise in enhancing the efficacy and safety of thyroiditis treatments. By encapsulating therapeutic agents within nanoparticles and directing them specifically to the affected thyroid tissue, researchers aim to minimize systemic side effects and optimize drug concentrations at the site of inflammation.
- Microbiome Modulation: Growing evidence suggests that the gut microbiome plays a role in regulating immune function and inflammation, implicating dysbiosis (imbalance) in the development and progression of autoimmune thyroid disorders. Therapies aimed at modulating the gut microbiota, such as probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation, hold the potential for attenuating autoimmune responses and alleviating symptoms of thyroiditis.
Future Directions
- Targeting Novel Pathways: Ongoing research efforts focus on identifying novel molecular targets and pathways implicated in thyroiditis pathogenesis, paving the way for the development of innovative therapeutic agents that modulate immune responses and restore thyroid homeostasis.
- Combination Therapies: Combining multiple therapeutic modalities, such as immunomodulatory agents, hormone replacement therapy, and regenerative approaches, may offer synergistic benefits and improve outcomes for patients with refractory or severe thyroiditis.
- Personalized Vaccines: The concept of personalized vaccines, tailored to target specific autoantigens implicated in autoimmune thyroiditis, represents a promising avenue for inducing immune tolerance and halting disease progression in susceptible individuals.
- Biomarker Discovery: Advancements in biomarker discovery and validation hold the potential for facilitating early diagnosis, predicting disease progression, and monitoring treatment response in thyroiditis patients. Biomarker panels incorporating genetic, epigenetic, and proteomic markers may enhance precision medicine approaches and inform therapeutic decision-making.
- Patient-Centered Research: Emphasizing patient-centered research and incorporating patient perspectives into clinical trials and treatment development processes can ensure that therapeutic interventions align with patients’ priorities, preferences, and needs, ultimately improving adherence and outcomes.
Conclusion
Research advances in thyroiditis herald a new era of innovation and hope for patients grappling with these complex and often debilitating conditions. From immunomodulatory therapies and regenerative medicine approaches to precision medicine and microbiome modulation, the landscape of thyroiditis treatment is evolving rapidly, offering promising avenues for improved outcomes and quality of life. As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of thyroiditis pathogenesis and explore novel therapeutic strategies, the future holds great promise for transforming the lives of individuals affected by these disorders.