Research Advances In Thyroid Nodule Diagnosis And Treatment
Thyroid nodules, characterized by abnormal growths or lumps within the thyroid gland, represent a common medical condition affecting millions of people worldwide. While the majority of thyroid nodules are benign, a small percentage may harbor malignancy, necessitating accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Over the years, significant advancements in medical research have revolutionized the approach to thyroid nodule evaluation, diagnosis, and management. In this article, we explore some of the latest research breakthroughs in the field of thyroid nodule diagnosis and treatment, shedding light on the innovative techniques and strategies that are shaping the future of thyroid care.
Cutting-Edge Imaging Technologies
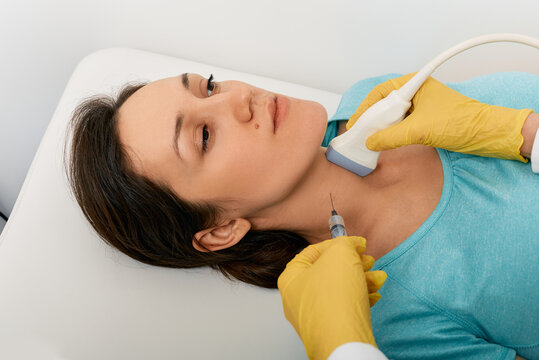
High-Resolution Ultrasound: Recent advancements in ultrasound technology have enabled clinicians to visualize thyroid nodules with unprecedented clarity and detail. High-resolution ultrasound allows for the precise characterization of nodules based on size, shape, echogenicity, and vascularity, aiding in the differentiation between benign and malignant lesions.
Shear Wave Elastography (SWE): SWE is a novel ultrasound technique that measures tissue stiffness, providing valuable information about the elasticity of thyroid nodules. Malignant nodules often exhibit increased stiffness compared to benign nodules, allowing for more accurate risk stratification and targeted biopsy selection.
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS): CEUS involves the administration of microbubble contrast agents to enhance the visualization of blood flow within thyroid nodules. This technique can help distinguish between benign and malignant nodules based on their vascular patterns, improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing unnecessary biopsies.
Molecular Testing and Biomarkers
Thyroid Nodule Molecular Profiling: Molecular testing of thyroid nodules involves analyzing genetic mutations, gene expression patterns, and molecular biomarkers to predict the risk of malignancy. Advanced molecular profiling techniques, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR), can provide valuable insights into the molecular alterations driving thyroid tumorigenesis, guiding treatment decisions and prognostication.
Thyroid Nodule Gene Expression Panels: Commercially available gene expression panels, such as the Afirma Gene Expression Classifier and ThyroSeq, utilize molecular signatures to stratify thyroid nodules into low, intermediate, or high-risk categories for malignancy. These tests help clinicians identify which nodules may safely undergo observation or require further evaluation with biopsy.
Minimally Invasive Therapies
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): RFA is a minimally invasive procedure that uses thermal energy to destroy thyroid nodules. This technique is particularly effective for treating symptomatic or cosmetically bothersome benign nodules, offering a safe and well-tolerated alternative to surgery.
Ethanol Ablation: Ethanol ablation involves the injection of ethanol (alcohol) directly into thyroid nodules to induce necrosis and shrinkage. This technique is commonly used for the treatment of cystic or predominantly cystic nodules, with high rates of success and low complication rates.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD): CAD systems utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to assist radiologists in the interpretation of imaging studies. These systems can analyze ultrasound images of thyroid nodules and provide quantitative assessments of nodule characteristics, improving diagnostic accuracy and consistency.
Predictive Modeling and Risk Stratification: Machine learning algorithms can analyze clinical, imaging, and molecular data to develop predictive models for thyroid nodule diagnosis and prognosis. These models can help clinicians identify high-risk nodules for early intervention and personalize treatment approaches based on individual patient characteristics.
Future Directions and Challenges
While research advancements in thyroid nodule diagnosis and treatment have been promising, several challenges remain on the horizon. These include the need for further validation and standardization of novel diagnostic techniques, the integration of molecular testing into clinical practice, and the optimization of minimally invasive therapies for different types of thyroid nodules. Additionally, ongoing research efforts are focused on elucidating the underlying genetic and molecular mechanisms driving thyroid tumorigenesis, with the ultimate goal of developing targeted therapies and precision medicine approaches for thyroid cancer.
In conclusion, research breakthroughs in thyroid nodule diagnosis and treatment are transforming the landscape of thyroid care, offering new opportunities for early detection, risk stratification, and personalized management. By leveraging cutting-edge imaging technologies, molecular testing, minimally invasive therapies, and artificial intelligence, clinicians can improve diagnostic accuracy, enhance treatment outcomes, and optimize patient care in the era of precision medicine. As research continues to advance, the future holds great promise for further innovation and progress in the field of thyroid nodule management.