Postpartum Thyroiditis: What New Mothers Need To Know
Postpartum thyroiditis is a condition that affects the thyroid gland, an essential part of the endocrine system, in women who have recently given birth. This condition, which occurs within the first year after delivery, can lead to both hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid). Understanding postpartum thyroiditis is crucial for new mothers as it can significantly impact their health and well-being.
What is Postpartum Thyroiditis?
Postpartum thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid gland that occurs after childbirth. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and other vital bodily functions. In postpartum thyroiditis, the inflammation can cause the gland to initially release too much thyroid hormone, leading to hyperthyroidism. This phase is usually followed by a period of hypothyroidism, where the gland produces too little hormone.
Phases of Postpartum Thyroiditis
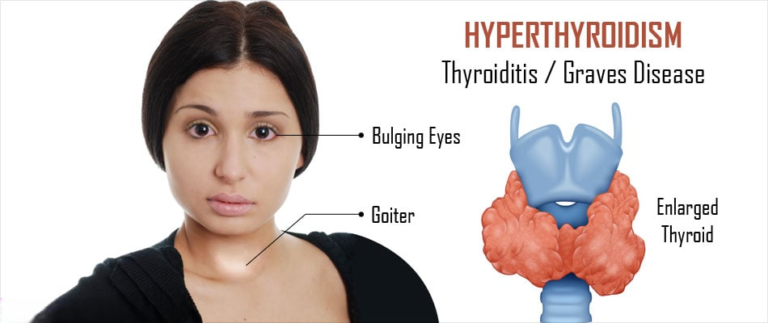
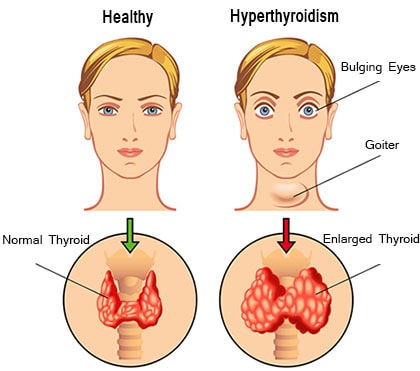
Hyperthyroid Phase: This phase typically occurs between one and four months postpartum and can last for one to three months. During this period, the inflamed thyroid gland releases an excess of thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. Symptoms may include:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Unexplained weight loss
- Anxiety and irritability
- Increased sensitivity to heat
- Fatigue
- Tremors
2. Hypothyroid Phase: Following the hyperthyroid phase, the thyroid gland’s hormone production slows down, often leading to hypothyroidism. This phase generally occurs between four and eight months postpartum and can also last for one to three months. Symptoms of hypothyroidism may include:
- Weight gain
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Depression
- Dry skin
- Constipation
- Cold intolerance
3. Euthyroid Phase: After the hypothyroid phase, many women’s thyroid function returns to normal, entering what is known as the euthyroid phase. However, in some cases, hypothyroidism may become permanent, requiring lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Causes and Risk Factors
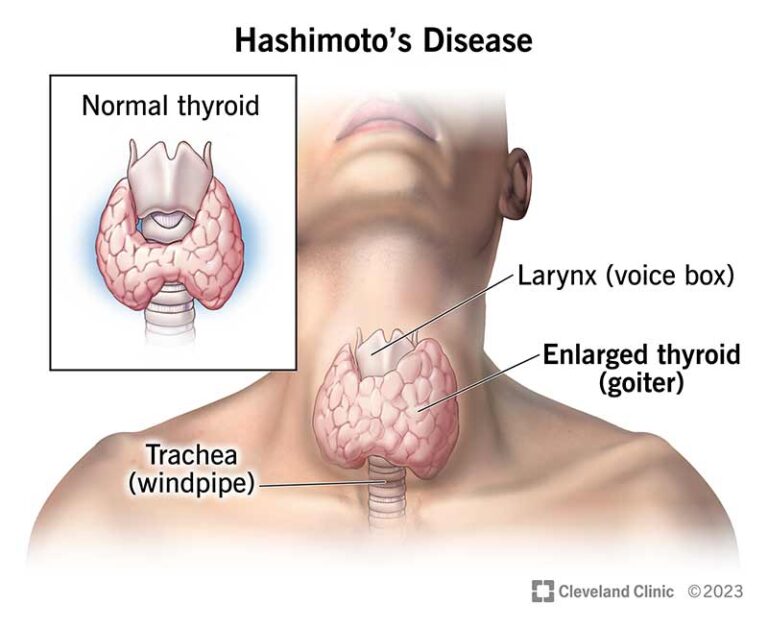
The exact cause of postpartum thyroiditis is not well understood, but it is believed to be an autoimmune condition similar to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. The immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and altered thyroid hormone production. Several factors can increase the risk of developing postpartum thyroiditis, including:
- A history of thyroid dysfunction
- Presence of thyroid antibodies (anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies)
- Type 1 diabetes or other autoimmune disorders
- A family history of thyroid disease
- Previous episodes of postpartum thyroiditis
Diagnosis
Diagnosing postpartum thyroiditis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Physicians typically begin with a thorough medical history and physical examination, focusing on the symptoms presented by the patient. Blood tests are crucial in confirming the diagnosis and may include:
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH): High levels indicate hypothyroidism, while low levels suggest hyperthyroidism.
- Free T4 and Free T3: These tests measure the actual levels of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream.
- Thyroid antibodies: The presence of anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies supports the diagnosis of autoimmune thyroiditis.
Treatment
Treatment for postpartum thyroiditis depends on the phase and severity of the condition. Some women may not require any treatment if their symptoms are mild and transient. However, when intervention is necessary, it may include:
1. Hyperthyroid Phase:
- Beta-blockers: These medications, such as propranolol, can help manage symptoms like rapid heart rate and tremors by blocking the effects of thyroid hormones on the body.
- Antithyroid medications: In rare and severe cases, antithyroid drugs may be used, but this is uncommon for postpartum thyroiditis.
2. Hypothyroid Phase:
- Thyroid hormone replacement therapy: Levothyroxine is the standard treatment for hypothyroidism. It replaces the deficient thyroid hormone and helps normalize metabolic functions.
Regular monitoring of thyroid function tests is essential to adjust treatment and ensure optimal thyroid hormone levels. Women with postpartum thyroiditis should have their thyroid function checked every few months until it stabilizes.
Impact on New Mothers
Postpartum thyroiditis can significantly impact a new mother’s physical and emotional health. Symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, and mood swings can be particularly challenging during the postpartum period, a time already marked by significant adjustments and demands. Managing these symptoms effectively is crucial for the well-being of both the mother and her baby.
Breastfeeding Considerations
Most treatments for postpartum thyroiditis are compatible with breastfeeding. Beta-blockers and thyroid hormone replacement therapy are generally considered safe, but it’s important for mothers to discuss their treatment options with their healthcare provider to ensure the safety of their baby.
Long-term Outlook
For many women, postpartum thyroiditis is a temporary condition, and thyroid function returns to normal within 12 to 18 months after delivery. However, some women may develop permanent hypothyroidism and require lifelong treatment. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential to monitor thyroid function and adjust treatment as needed.
Preventive Measures and Monitoring
Women with risk factors for postpartum thyroiditis should be closely monitored during pregnancy and after delivery. Early detection and management can help mitigate the impact of the condition. Preventive measures include:
- Regular thyroid function tests during pregnancy and postpartum
- Screening for thyroid antibodies in women with a history of thyroid dysfunction or autoimmune disorders
- Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle to support overall thyroid health
Conclusion
Postpartum thyroiditis is a relatively common but often underdiagnosed condition that can significantly affect new mothers. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and effective management. With appropriate care and monitoring, most women can achieve a full recovery and maintain their thyroid health. New mothers experiencing unusual symptoms after childbirth should seek medical advice to ensure their well-being and that of their baby.