Postpartum Thyroiditis: Impact On New Mothers
Postpartum thyroiditis is a condition that affects the thyroid gland, typically occurring within the first year after childbirth. It involves inflammation of the thyroid gland, leading to transient hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid) followed by hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid). This condition can have significant implications for new mothers, affecting their physical health, emotional well-being, and overall postpartum experience. In this article, we explore the impact of postpartum thyroiditis on new mothers and discuss management strategies for this common yet often overlooked condition.
Understanding Postpartum Thyroiditis
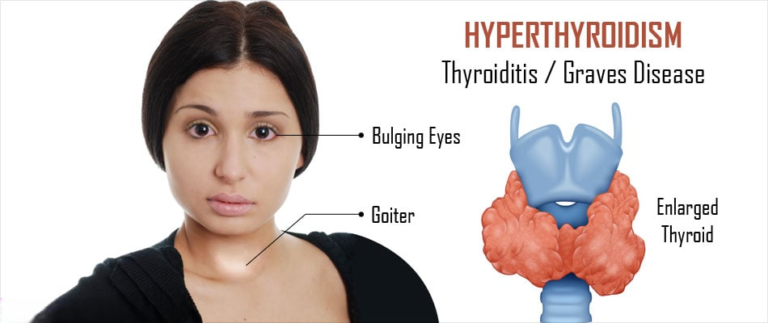
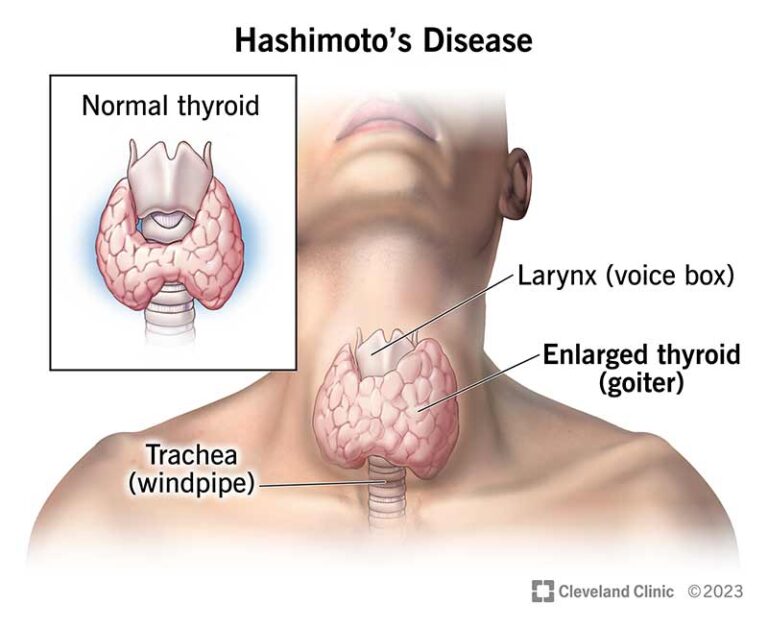
Postpartum thyroiditis is a relatively common condition, affecting approximately 5-10% of women within the first year after giving birth. It typically presents in two phases: an initial phase of hyperthyroidism, characterized by symptoms such as anxiety, palpitations, and weight loss, followed by a phase of hypothyroidism, marked by fatigue, weight gain, and depression. Some women may experience only one phase of the condition, while others may progress through both phases.
Impact on Physical Health
The fluctuations in thyroid hormone levels associated with postpartum thyroiditis can have a profound impact on a new mother’s physical health. During the hyperthyroid phase, women may experience symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, tremors, and excessive sweating, which can be distressing and disruptive to daily life. Conversely, the hypothyroid phase may cause fatigue, weakness, and difficulty concentrating, making it challenging to care for a newborn and manage household responsibilities.
Emotional Well-Being
In addition to its effects on physical health, postpartum thyroiditis can also take a toll on a new mother’s emotional well-being. The hormonal fluctuations associated with thyroid dysfunction can exacerbate mood swings, anxiety, and depression, which are already common during the postpartum period. Feelings of overwhelm, irritability, and sadness may be heightened, making it crucial for new mothers to receive adequate support and understanding from healthcare providers, partners, and loved ones.
Breastfeeding Considerations
For women who are breastfeeding, postpartum thyroiditis may present additional challenges. Thyroid hormone imbalances can impact milk production and quality, potentially affecting the infant’s nutritional intake and growth. It is essential for breastfeeding mothers with postpartum thyroiditis to work closely with healthcare providers to monitor thyroid function and ensure optimal management while maintaining breastfeeding goals.
Long-Term Implications
While postpartum thyroiditis typically resolves within 12 to 18 months after onset, some women may develop persistent thyroid dysfunction requiring ongoing management. Untreated hypothyroidism can lead to complications such as fatigue, weight gain, and cognitive impairment, impacting a woman’s quality of life and ability to engage fully in daily activities. Regular monitoring of thyroid function and appropriate treatment are essential for preventing long-term complications and promoting overall well-being.
Management Strategies
The management of postpartum thyroiditis involves a multidisciplinary approach, including close monitoring of thyroid function, symptomatic treatment, and supportive care. Healthcare providers may recommend thyroid hormone replacement therapy during the hypothyroid phase to alleviate symptoms and restore thyroid hormone levels to normal. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as stress management, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet can help support thyroid health and overall well-being.
Support and Education
Supportive care and education are crucial components of managing postpartum thyroiditis. New mothers should be encouraged to seek support from healthcare providers, support groups, and peer networks to navigate the challenges of thyroid dysfunction during the postpartum period. Education about the signs and symptoms of postpartum thyroiditis, as well as its potential impact on physical and emotional health, empowers women to advocate for their own care and seek timely intervention when needed.
Conclusion
Postpartum thyroiditis is a common yet often overlooked condition that can have significant implications for new mothers. Its impact extends beyond physical health to include emotional well-being, breastfeeding, and long-term thyroid function. By raising awareness of postpartum thyroiditis and providing comprehensive support and management strategies, healthcare providers can help new mothers navigate this challenging condition and achieve optimal health and wellness during the postpartum period and beyond.