Managing Hypothyroidism In The Elderly Population
Hypothyroidism, a common endocrine disorder characterized by inadequate thyroid hormone production, poses unique challenges in the elderly population. As individuals age, the prevalence of hypothyroidism increases, and managing this condition becomes crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. In this article, we delve into the complexities of managing hypothyroidism in the elderly, exploring diagnostic considerations, treatment approaches, and potential complications.
Understanding Hypothyroidism in the Elderly
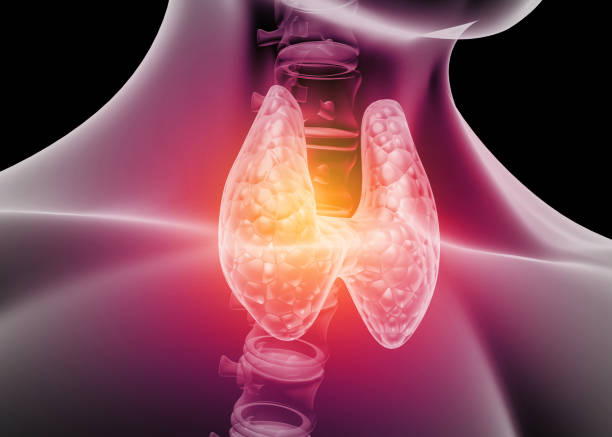
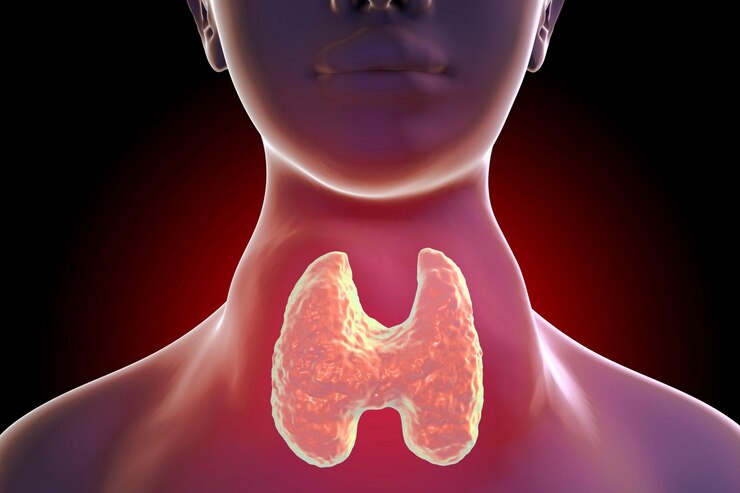
Hypothyroidism is more prevalent in older adults, with estimates suggesting that up to 20% of individuals over the age of 60 may have subclinical or overt hypothyroidism. Aging is associated with changes in thyroid function, including alterations in hormone levels and increased susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Additionally, comorbidities and medication use in the elderly population can impact thyroid function and complicate management.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Diagnosing hypothyroidism in older adults requires careful consideration of age-related changes in thyroid function and the presence of comorbidities. While symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cognitive impairment may overlap with typical signs of hypothyroidism, they can also be attributed to other age-related conditions. Therefore, thorough clinical evaluation and interpretation of thyroid function tests are essential for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Considerations
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy remains the cornerstone of hypothyroidism management in the elderly population. However, initiating and titrating therapy requires careful monitoring to avoid adverse effects such as cardiac arrhythmias and exacerbation of osteoporosis, which are more prevalent in older adults. Furthermore, drug interactions with other medications commonly used in the elderly population, such as cardiovascular drugs and anticoagulants, must be taken into account when prescribing thyroid hormone replacement.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring of thyroid function is essential to ensure optimal treatment outcomes and prevent complications in elderly patients with hypothyroidism. Thyroid function tests should be performed periodically to assess hormone levels and adjust medication dosage as needed. Additionally, clinical assessment of symptoms and signs of overtreatment or undertreatment is crucial for maintaining euthyroid status and improving quality of life.
Complications and Challenges
Managing hypothyroidism in the elderly population is not without challenges. Aging-related changes in metabolism and organ function can affect the pharmacokinetics of thyroid hormone replacement medications, necessitating individualized treatment approaches. Moreover, older adults may be more susceptible to adverse effects of thyroid hormone therapy, such as cardiac complications and exacerbation of preexisting conditions.
Lifestyle Factors and Supportive Care
In addition to pharmacological treatment, lifestyle modifications, and supportive care play a vital role in managing hypothyroidism in the elderly. Nutritional interventions, including adequate iodine intake and supplementation with selenium and vitamin D, may support thyroid function and improve overall health outcomes. Furthermore, promoting physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes can help optimize treatment outcomes and enhance quality of life.
Conclusion
Managing hypothyroidism in the elderly population requires a comprehensive approach that considers age-related changes in thyroid function, comorbidities, and medication use. By understanding the complexities of hypothyroidism in older adults and addressing treatment challenges with tailored interventions, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for elderly patients with this common endocrine disorder. Through collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, patients, and caregivers, effective management of hypothyroidism in the elderly can be achieved, enabling individuals to age gracefully and maintain optimal thyroid health.