Emerging Trends In Thyroid Tumour Research
Thyroid tumors represent a significant health concern worldwide, with both benign and malignant forms posing diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Over the years, advancements in research have shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying thyroid tumorigenesis, paving the way for innovative approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and management. In this article, we delve into the latest trends and breakthroughs in thyroid tumor research, exploring promising avenues for improved understanding and management of these complex diseases.
Understanding Thyroid Tumors
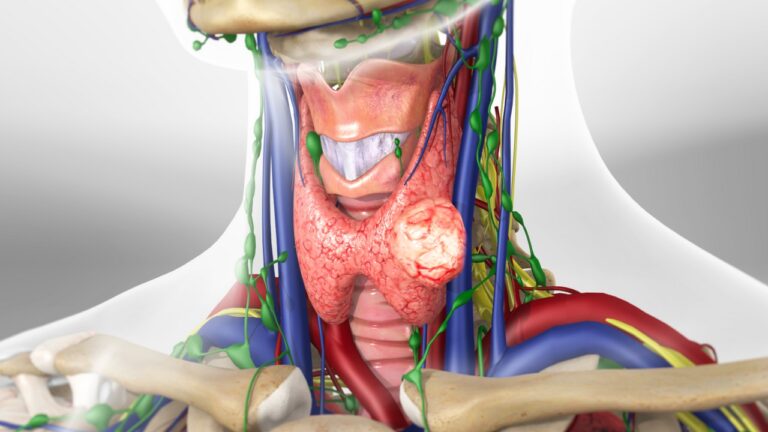
Thyroid tumors encompass a spectrum of neoplastic conditions, ranging from benign nodules to malignant thyroid cancers. While most thyroid nodules are non-cancerous (benign), a small percentage may harbor malignant potential, necessitating thorough evaluation and management.
Emerging Trends in Thyroid Tumor Research
- Molecular Profiling and Biomarkers:
Recent advancements in molecular profiling techniques have enabled the comprehensive characterization of thyroid tumors at the molecular level. Identification of specific genetic alterations, such as mutations in genes like BRAF, RAS, and RET, has facilitated the development of molecular biomarkers for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic purposes. - Precision Medicine Approaches:
The advent of precision medicine approaches, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies, has revolutionized the treatment landscape for advanced or recurrent thyroid cancers. Targeted agents directed against specific molecular targets, such as BRAF inhibitors or tyrosine kinase inhibitors, have shown promising results in selected patient populations. - Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors:
Immunotherapy, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) or its ligand (PD-L1), has emerged as a novel therapeutic strategy for advanced thyroid cancers. These agents harness the body’s immune system to target and destroy cancer cells, offering a new treatment option for patients who have failed conventional therapies. - Imaging Modalities and Radiomics:
Advancements in imaging modalities, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET), coupled with the emerging field of radiomics, hold promise for non-invasive characterization and risk stratification of thyroid nodules. Radiomics involves the extraction of quantitative features from medical images to predict tumor behavior and guide treatment decisions. - Liquid Biopsies and Circulating Biomarkers:
The development of non-invasive diagnostic approaches, such as liquid biopsies and circulating biomarkers, offers a promising alternative to traditional tissue biopsies for monitoring disease progression and treatment response in thyroid cancer patients. Detection of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) or microRNAs in peripheral blood may provide valuable insights into tumor dynamics and therapeutic efficacy.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The integration of these emerging trends in thyroid tumor research holds significant clinical implications for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of thyroid cancers. By leveraging molecular profiling, precision medicine approaches, immunotherapy, advanced imaging techniques, and liquid biopsies, clinicians can tailor treatment strategies to individual patient characteristics and optimize outcomes.
Conclusion
The landscape of thyroid tumor research is evolving rapidly, driven by innovative technologies, collaborative efforts, and a deeper understanding of tumor biology. By embracing emerging trends and breakthroughs in molecular profiling, precision medicine, immunotherapy, imaging modalities, and liquid biopsies, we are poised to usher in a new era of personalized and targeted therapies for thyroid cancers. As researchers and clinicians continue to unravel the complexities of thyroid tumorigenesis, the future holds great promise for improved outcomes and quality of life for patients affected by these diseases.