Emerging Therapies For Thyroiditis: Harnessing The Potential Of Immunomodulatory Agents
Thyroiditis, an inflammatory condition affecting the thyroid gland, encompasses a spectrum of disorders with diverse etiologies, manifestations, and treatment challenges. Among the exciting developments in thyroiditis management are emerging immunomodulatory therapies. These novel treatments aim to target the underlying immune dysregulation implicated in various types of thyroiditis, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals. In this article, we delve into the landscape of emerging immunomodulatory agents and their potential in transforming thyroiditis management.
Understanding Thyroiditis and Immunomodulation
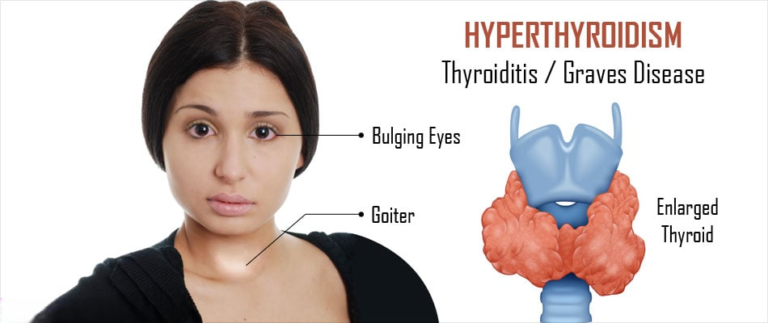
Thyroiditis encompasses conditions characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland, including autoimmune thyroiditis such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, subacute thyroiditis, and postpartum thyroiditis. While conventional treatments often focus on symptom management and hormone replacement, emerging therapies seek to modulate the immune response underlying thyroid inflammation. By targeting specific immune pathways, these therapies aim to mitigate thyroid gland damage and halt disease progression.
The Promise of Immunomodulatory Agents
Immunomodulatory agents represent a diverse class of medications designed to modulate immune responses, ranging from cytokine inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies to small molecule inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors. While many of these agents were initially developed for other autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis, their potential utility in thyroiditis has garnered increasing attention.
Targeting Immune Pathways
One approach in emerging thyroiditis therapies involves targeting key immune pathways implicated in disease pathogenesis. For example, monoclonal antibodies against pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) or interleukin-6 (IL-6) have shown promise in reducing inflammation and ameliorating symptoms in certain types of thyroiditis. Similarly, agents targeting B-cell or T-cell pathways involved in autoantibody production and immune cell activation hold the potential for modulating immune responses in autoimmune thyroiditis.
Clinical Trials and Evidence
Clinical trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of emerging immunomodulatory agents in thyroiditis are underway, providing valuable insights into their potential benefits and limitations. Preliminary data from early-phase trials suggest encouraging results, with some agents demonstrating significant reductions in thyroid inflammation, improvement in thyroid function, and reduction in autoantibody levels. However, large-scale randomized controlled trials are needed to establish the long-term efficacy and safety of these therapies.
Personalized Approaches to Treatment
One of the hallmarks of emerging immunomodulatory therapies is their potential for personalized treatment approaches. By targeting specific immune pathways or molecular targets, these therapies may offer tailored solutions for individuals with different types and manifestations of thyroiditis. Biomarker-driven approaches, including genetic profiling and immune cell profiling, may help identify patients who are most likely to benefit from specific immunomodulatory agents, optimizing treatment selection and response.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their promise, emerging immunomodulatory therapies face several challenges and considerations. These include concerns regarding long-term safety, the potential for immune-related adverse events, and the accessibility and affordability of novel medications. Additionally, the heterogeneity of thyroiditis phenotypes and the complexity of immune dysregulation pose challenges for identifying optimal treatment strategies and predicting individual responses.
Integration with Existing Therapies
Emerging immunomodulatory therapies are not intended to replace existing treatments for thyroiditis but rather to complement them. For individuals who do not achieve adequate symptom control or disease remission with conventional therapies, immunomodulatory agents may offer additional options for disease management. Integration with existing treatments, including hormone replacement therapy and supportive care measures, is essential to optimize outcomes and ensure comprehensive patient care.
Looking Ahead
As research in immunology and autoimmune disease continues to advance, the landscape of thyroiditis management is poised for transformation. Emerging immunomodulatory agents represent a promising frontier in the quest for more effective and targeted therapies for thyroiditis. By harnessing the potential of these novel treatments, clinicians and researchers are paving the way toward a future where individuals with thyroiditis can benefit from personalized, precision medicine approaches that address the underlying immune dysregulation driving disease pathogenesis.