Emerging Therapies And Research In Thyroid Tumor Treatment
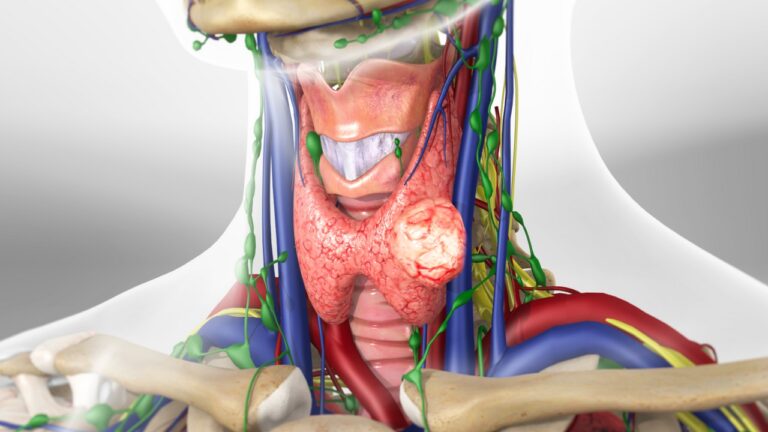
Thyroid tumors encompass a spectrum of neoplastic conditions ranging from benign nodules to malignant thyroid cancer. While conventional treatment modalities such as surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and thyroid hormone replacement have been the mainstays of management, ongoing research efforts are continuously uncovering novel therapeutic approaches and innovations aimed at improving outcomes for patients with thyroid tumors. In this article, we delve into the latest advancements in thyroid tumor treatment, exploring emerging therapies and cutting-edge research shaping the field.
Precision Medicine and Targeted Therapies
Precision medicine has revolutionized the approach to cancer treatment by tailoring therapies to the molecular characteristics of individual tumors. In the realm of thyroid cancer, targeted therapies that selectively inhibit aberrant signaling pathways implicated in tumor growth and progression have shown promise in improving outcomes, particularly in advanced or refractory cases. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as sorafenib and lapatinib, have demonstrated efficacy in treating radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR) and other molecular targets. Furthermore, molecular profiling techniques, including next-generation sequencing (NGS), enable the identification of actionable genetic alterations in thyroid tumors, guiding the selection of targeted therapies and personalized treatment regimens for patients.
Immunotherapy and Checkpoint Inhibitors
Immunotherapy has emerged as a transformative approach to cancer treatment, harnessing the body’s immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. Checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, block inhibitory pathways that suppress immune responses, allowing T cells to mount an effective anti-tumor immune response. While immunotherapy has demonstrated remarkable success in various malignancies, its efficacy in thyroid cancer, particularly in aggressive forms such as anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC), remains an area of active investigation. Early clinical trials evaluating the use of checkpoint inhibitors alone or in combination with other modalities have shown promising results, suggesting a potential role for immunotherapy in the management of advanced or recurrent thyroid tumors.
Radioembolization and Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT)
Radioembolization, also known as selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT), involves the administration of radioactive microspheres directly into the arterial supply of tumors, leading to localized radiation delivery and tumor destruction. In the context of thyroid cancer, particularly metastatic or unresectable disease, radioembolization offers a minimally invasive and targeted approach to delivering therapeutic radiation to tumor sites while sparing surrounding healthy tissues. This modality is particularly beneficial for patients with radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer or those who are not candidates for surgery or external beam radiotherapy. Ongoing research is evaluating the safety, efficacy, and long-term outcomes of radioembolization in the management of advanced thyroid tumors, with the potential for expanding its use in clinical practice.
Nano-based Drug Delivery Systems
Nano-based drug delivery systems represent a promising approach to enhancing the efficacy and minimizing the toxicity of anti-cancer therapies in thyroid tumors. Nanoformulations, such as liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles, and dendrimers, can encapsulate therapeutic agents and deliver them selectively to tumor cells, maximizing drug concentration at the target site while reducing systemic exposure and off-target effects. Additionally, nano-carriers can overcome biological barriers, such as the blood-brain barrier or multidrug resistance mechanisms, enhancing drug penetration and bioavailability within tumors. Preclinical studies have demonstrated the feasibility and efficacy of nano-based drug delivery systems in delivering chemotherapy agents, targeted therapies, and radioisotopes for the treatment of thyroid cancer, with the potential for translation into clinical applications in the future.
Gene Editing and Therapeutic Approaches
Advancements in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, hold promise for developing novel therapeutic approaches for thyroid tumors by targeting specific genetic alterations implicated in tumor development and progression. CRISPR-based gene editing enables precise modification of the genome, allowing for the correction of genetic mutations, disruption of oncogenic pathways, and modulation of immune responses against cancer cells. In the context of thyroid cancer, CRISPR-mediated knockout of driver oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes, such as BRAF or TP53, could potentially inhibit tumor growth and sensitize cancer cells to existing therapies. Moreover, CRISPR-based screening approaches facilitate the identification of synthetic lethal interactions and novel therapeutic targets in thyroid tumors, paving the way for the development of personalized treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Emerging therapies and research initiatives are transforming the landscape of thyroid tumor treatment, offering new hope for patients with both benign and malignant thyroid nodules. From precision medicine and targeted therapies to immunotherapy, radioembolization, nano-based drug delivery systems, and gene editing technologies, these advancements are revolutionizing the way thyroid tumors are diagnosed and managed. As research continues to unravel the molecular mechanisms driving thyroid tumorigenesis and therapeutic resistance, the future holds promise for further innovations that will improve outcomes, reduce treatment-related toxicity, and ultimately enhance the quality of life for patients with thyroid tumors.