Emerging Therapies And Research In The Treatment Of Thyroid Tumors
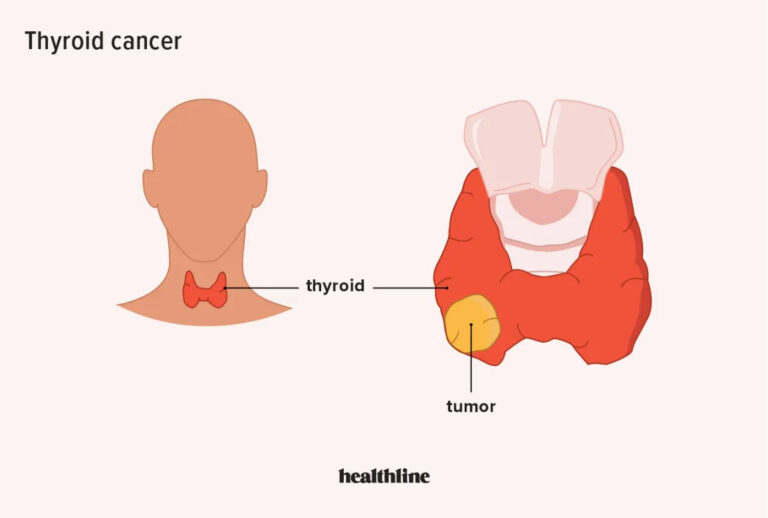
Thyroid tumors encompass a spectrum of conditions ranging from benign nodules to malignant cancers, presenting a significant challenge in clinical management. While traditional treatment approaches such as surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and thyroid hormone suppression have been mainstays in the management of thyroid tumors, emerging therapies and ongoing research offer new avenues for improved outcomes. This article explores the latest advancements in the treatment of thyroid tumors, highlighting emerging therapies and cutting-edge research endeavors.
Advancements in Targeted Therapies
One of the most promising developments in the treatment of thyroid tumors is the advent of targeted therapies aimed at specific molecular pathways involved in tumor growth and progression. Thyroid cancers often harbor genetic alterations, such as mutations in the BRAF, RAS, and RET genes, which drive tumorigenesis and confer resistance to traditional therapies. Targeted agents that inhibit these oncogenic pathways have shown efficacy in clinical trials and are increasingly being integrated into the management of advanced thyroid cancers.
For example, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as sorafenib, lenvatinib, and vandetanib have demonstrated significant clinical benefits in patients with advanced, refractory thyroid cancers. These agents target key signaling pathways involved in tumor angiogenesis and cell proliferation, leading to tumor regression and improved progression-free survival. Additionally, selective RET inhibitors, such as selpercatinib and pralsetinib, have shown remarkable efficacy in patients with RET fusion-positive thyroid cancers, offering a personalized treatment approach based on tumor molecular profiling.
Immunotherapy Approaches
Another area of active investigation in the treatment of thyroid tumors is immunotherapy, which harnesses the body’s immune system to target and eliminate cancer cells. While thyroid cancers have traditionally been considered immunologically “cold” tumors with limited response to immunotherapy, recent studies have identified subsets of patients who may benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs).
Preliminary data from clinical trials suggest that ICIs, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, may have activity in a subset of patients with advanced thyroid cancers, particularly those with aggressive histological subtypes such as poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid carcinomas. By blocking inhibitory immune checkpoints, ICIs unleash the antitumor immune response, leading to durable responses and prolonged survival in select patients. Ongoing research is focused on identifying predictive biomarkers and combination strategies to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy in thyroid cancer.
Novel Radiopharmaceuticals
In addition to targeted therapies and immunotherapy, novel radiopharmaceuticals are being explored as potential treatment modalities for thyroid tumors, particularly radioactive iodine-refractory thyroid cancers. Radioactive iodine therapy has been a cornerstone of treatment for differentiated thyroid cancers; however, a subset of patients develop resistance to this therapy, limiting its efficacy. Emerging radiopharmaceuticals, such as lutetium-177 (^177Lu)-DOTA-TATE and iodine-131 (^131I)-MIBG, offer alternative approaches for targeted radionuclide therapy in advanced thyroid cancers.
These radiopharmaceuticals target overexpressed receptors on thyroid cancer cells, such as somatostatin receptors and norepinephrine transporters, delivering cytotoxic radiation directly to tumor cells while sparing surrounding healthy tissues. Early clinical trials have shown promising results with ^177Lu-DOTA-TATE and ^131I-MIBG in patients with metastatic thyroid cancers, including those refractory to conventional therapies. Further research is needed to optimize dosing regimens, evaluate long-term safety, and identify patients most likely to benefit from these novel radiopharmaceuticals.
Conclusion
The treatment landscape for thyroid tumors is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and novel radiopharmaceuticals. These emerging treatment modalities offer new hope for patients with advanced or refractory thyroid cancers, providing personalized and precision-based approaches to treatment. While challenges remain in terms of treatment resistance, toxicity management, and patient selection, ongoing research efforts hold promise for further improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by thyroid tumors. Collaborative efforts between clinicians, researchers, and industry partners are essential to translate these advancements into meaningful clinical benefits for patients with thyroid cancer.