Emerging Therapies And Research In Multinodular Goitre Treatment
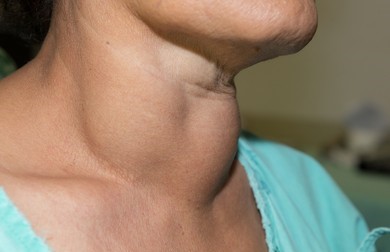
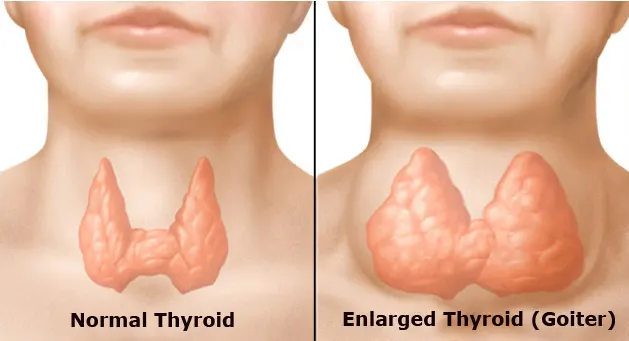
Multinodular goitre (MNG) represents a prevalent thyroid disorder characterized by the presence of multiple nodules within the thyroid gland. While conventional treatment options like surgery and thyroid hormone replacement therapy remain effective, emerging therapies and ongoing research are reshaping the landscape of MNG management. This article delves into the latest advancements in MNG treatment, shedding light on promising therapies and cutting-edge research endeavors.
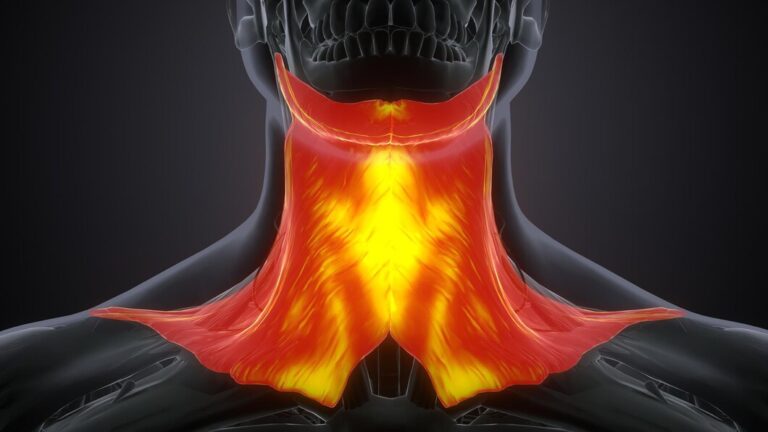
Understanding Multinodular Goitre
Before delving into emerging therapies, it’s crucial to understand the pathology and clinical manifestations of MNG. Multinodular goitre can lead to thyroid enlargement, causing symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, and neck discomfort. While the condition may not always require treatment, severe cases can lead to complications such as compression of nearby structures or thyroid dysfunction.
Current Treatment Landscape
Traditionally, treatment options for MNG have included observation, thyroid hormone replacement therapy, and surgery. Observation is often recommended for asymptomatic cases, while surgery may be necessary for symptomatic or malignant nodules. Thyroid hormone replacement therapy aims to suppress thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels, potentially reducing the growth of thyroid nodules.
Emerging Therapies
a. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA):
Radiofrequency ablation involves using heat generated by radiofrequency waves to destroy thyroid nodules. This minimally invasive procedure has shown promising results in reducing nodule size and alleviating symptoms in patients with MNG. RFA offers a safer alternative to surgery for individuals who are not suitable candidates for thyroidectomy.
b. Ethanol Ablation (EA):
Ethanol ablation involves injecting ethanol directly into thyroid nodules, causing them to shrink over time. This technique is particularly effective for cystic nodules and has been shown to improve symptoms and cosmetic outcomes in MNG patients. Ethanol ablation is well-tolerated and can be performed on an outpatient basis.
c. Laser Ablation:
Laser ablation utilizes laser energy to heat and destroy thyroid nodules. This emerging therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reducing nodule volume and improving symptoms in patients with MNG. Laser ablation offers a minimally invasive alternative to surgery, with fewer complications and a shorter recovery period.
d. Thyroid Artery Embolization (TAE):
Thyroid artery embolization involves blocking the blood supply to thyroid nodules, leading to their shrinkage and resolution of symptoms. This non-surgical approach has shown promising results in reducing nodule size and relieving compressive symptoms in patients with MNG. TAE is particularly beneficial for individuals who are not surgical candidates or prefer a less invasive treatment option.
Ongoing Research
In addition to emerging therapies, ongoing research endeavors are focused on elucidating the underlying mechanisms of MNG and identifying novel treatment targets. Areas of interest include:
a. Genetic Studies:
Genetic studies aim to identify genetic mutations associated with MNG development and progression. By understanding the genetic basis of MNG, researchers can develop targeted therapies tailored to individual patients’ genetic profiles.
b. Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy involves harnessing the body’s immune system to target and destroy cancerous or abnormal cells, including thyroid nodules. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy of immunotherapy agents in treating MNG and preventing disease recurrence.
c. Molecular Targeted Therapy:
Molecular targeted therapy aims to inhibit specific molecular pathways involved in MNG pathogenesis. By targeting key signaling pathways, such as the MAPK pathway, researchers hope to develop more effective and targeted therapies for MNG treatment.
d. Stem Cell Therapy:
Stem cell therapy holds the potential for regenerating thyroid tissue and restoring thyroid function in patients with MNG. Preclinical studies have shown promising results, but further research is needed to validate the safety and efficacy of stem cell-based approaches in clinical settings.
Conclusion
Emerging therapies and ongoing research are revolutionizing the field of MNG treatment, offering new hope for patients with this debilitating condition. From minimally invasive procedures like radiofrequency ablation to targeted molecular therapies, the future of MNG management looks promising. By embracing innovation and collaboration, healthcare professionals can continue to improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for individuals living with MNG.