Emerging Research In Thyroid Nodule Detection And Treatment
Thyroid nodules, though often benign, present a significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenge in clinical practice. With emerging research, innovative approaches to detect and treat thyroid nodules are continuously evolving. This article explores recent advancements in the field, shedding light on novel diagnostic techniques, therapeutic modalities, and promising avenues for future research.
Understanding Thyroid Nodules
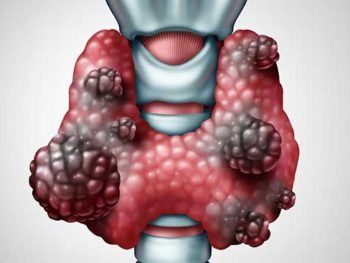
Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths within the thyroid gland, ranging from small, asymptomatic nodules to larger ones causing symptoms such as neck swelling or difficulty swallowing. While most nodules are benign, a small percentage may harbor malignancy, necessitating accurate detection and appropriate management.
Diagnostic Innovations
Traditionally, thyroid nodules are evaluated using ultrasound imaging and fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB). However, emerging technologies offer enhanced diagnostic accuracy and precision. One such innovation is shear wave elastography, which measures tissue stiffness, aiding in distinguishing between benign and malignant nodules. Additionally, molecular testing of FNAB samples for genetic mutations associated with thyroid cancer has shown promise in improving diagnostic specificity.
Imaging Modalities
Beyond conventional ultrasound, advanced imaging modalities are revolutionizing thyroid nodule assessment. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) provides real-time visualization of vascularity within nodules, aiding in characterizing their nature. Furthermore, techniques like diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) offer valuable insights into tissue microstructure, complementing traditional imaging approaches.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications
AI-driven algorithms are increasingly integrated into thyroid nodule evaluation, offering rapid and accurate analysis of imaging data. Machine learning models trained on large datasets can assist radiologists in identifying suspicious features and predicting malignancy risk, thereby optimizing clinical decision-making.
Therapeutic Innovations
Treatment of thyroid nodules depends on factors such as size, symptoms, and malignancy risk. While surgery and radioiodine therapy remain the mainstays of management, emerging therapeutic modalities offer less invasive alternatives. Thermal ablation techniques, including radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and laser ablation, effectively reduce nodule volume while preserving surrounding thyroid tissue. These minimally invasive procedures are associated with shorter recovery times and lower complication rates compared to surgery.
Targeted Therapies
In cases where thyroid nodules are hormonally active or resistant to conventional treatments, targeted therapies directed at specific molecular pathways show promise. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as lapatinib and sorafenib have demonstrated efficacy in shrinking nodules and improving symptoms in patients with refractory thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors, is being investigated as a potential treatment modality for advanced thyroid cancer. By unleashing the immune system’s antitumor response, these agents hold the potential to improve outcomes in patients with aggressive disease.
Future Directions
As research in thyroid nodule detection and treatment continues to advance, several exciting avenues warrant exploration. Personalized medicine approaches, leveraging genomic profiling and biomarker analysis, may enable tailored therapeutic strategies based on individual tumor characteristics. Furthermore, ongoing clinical trials evaluating novel agents and combination therapies offer hope for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for patients with thyroid nodules.
Conclusion
The landscape of thyroid nodule detection and treatment is evolving rapidly, driven by innovative technologies and research initiatives. From advanced imaging modalities to targeted therapies and immunotherapy, emerging approaches hold the promise of more accurate diagnosis, minimally invasive interventions, and improved patient outcomes. By embracing these advancements and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, clinicians can usher in a new era of precision medicine in the management of thyroid nodules.