Emerging Research In Hypothyroidism: Promising Insights And Innovations
Hypothyroidism, a condition characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, affects millions of individuals worldwide. While traditional treatments such as hormone replacement therapy have been effective for many patients, ongoing research is shedding light on new insights and innovations in the management of hypothyroidism. In this article, we will explore some of the latest research findings and promising advancements in the field of hypothyroidism.
Understanding Hypothyroidism
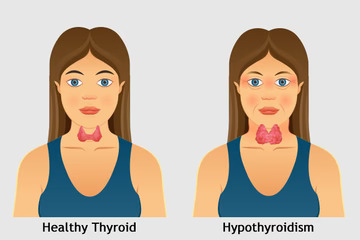
Before delving into emerging research, let’s first understand the basics of hypothyroidism. Hormones that control metabolism and other body processes are produced by the thyroid gland, which is situated in the neck. In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone, leading to a slowdown in metabolism and a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, constipation, and depression.
Current Treatment Approaches
Standard treatment for hypothyroidism typically involves hormone replacement therapy with synthetic thyroid hormones such as levothyroxine. This medication helps restore normal thyroid hormone levels in the body, alleviating symptoms and improving overall well-being. However, some patients may experience suboptimal responses to conventional treatment or struggle with medication adherence.
Promising Insights from Research
Recent research efforts have uncovered several intriguing insights into the pathophysiology of hypothyroidism and potential treatment avenues:
- Genetic Factors: Studies have identified genetic variations associated with an increased risk of hypothyroidism, offering insights into the underlying mechanisms of the condition and potential targets for personalized treatment approaches.
- Microbiome Influence: Emerging research suggests a link between the gut microbiome and thyroid function. Imbalances in gut bacteria may contribute to thyroid dysfunction, highlighting the potential role of probiotics and dietary interventions in managing hypothyroidism.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as iodine, selenium, and vitamin D, can impair thyroid function. Optimizing nutritional status through supplementation or dietary modifications may help improve thyroid hormone levels and alleviate symptoms.
- Environmental Exposures: Exposure to environmental toxins, including endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in plastics and pollutants, may disrupt thyroid function. Understanding the impact of environmental factors on thyroid health is an area of active research.
- Thyroid Autoimmunity: Autoimmune thyroid disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, are a common cause of hypothyroidism. Advances in understanding the underlying immune mechanisms and developing targeted immunomodulatory therapies hold promise for more effective treatment options.
Innovations in Hypothyroidism Management
In addition to insights gained from research, several innovative approaches to hypothyroidism management are being explored:
- Precision Medicine: Tailoring treatment regimens based on individual patient characteristics, including genetic profile, metabolic status, and lifestyle factors, holds the potential to optimize therapeutic outcomes and minimize side effects.
- Alternative Thyroid Hormone Formulations: Novel formulations of thyroid hormone replacement therapy, such as sustained-release formulations or combination therapies, are being investigated for their efficacy in improving symptom control and patient satisfaction.
- Non-Pharmacological Interventions: Complementary and alternative therapies, including acupuncture, herbal remedies, and mind-body practices, may offer adjunctive benefits for managing hypothyroidism symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
- Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: Advances in telemedicine technology enable remote monitoring of thyroid function and medication adherence, facilitating timely adjustments to treatment regimens and enhancing patient convenience.
- Regenerative Medicine: Experimental approaches involving stem cell therapy or tissue engineering hold the potential for regenerating damaged thyroid tissue and restoring normal thyroid function in patients with severe hypothyroidism.
Conclusion
The landscape of hypothyroidism management is evolving rapidly, driven by ongoing research efforts and innovative therapeutic approaches. From uncovering novel insights into the underlying mechanisms of the condition to exploring cutting-edge treatment modalities, the future holds great promise for improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals with hypothyroidism. By staying informed about emerging research findings and collaborating with healthcare providers, patients can take an active role in navigating the latest advancements in hypothyroidism care.