Emerging Research And Therapies In Hyperthyroidism Management
Hyperthyroidism, a condition characterized by excessive thyroid hormone production, affects millions of individuals worldwide. While conventional treatments such as medications, radioactive iodine therapy, and thyroidectomy have been mainstays in managing hyperthyroidism, ongoing research is uncovering new insights and therapeutic approaches. In this article, we explore the latest advancements in hyperthyroidism management, from innovative treatment modalities to promising research directions.
Understanding Hyperthyroidism
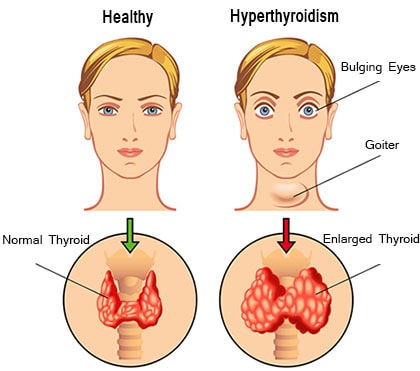
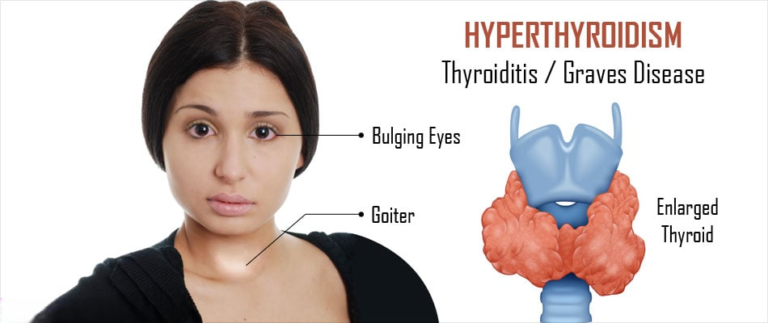
Before delving into emerging therapies, it’s essential to understand the underlying mechanisms of hyperthyroidism. The condition typically results from overactivity of the thyroid gland, which produces an excess of thyroid hormones, triiodothyronine (T3), and thyroxine (T4). This hormonal imbalance can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including rapid heartbeat, weight loss, heat intolerance, and nervousness.
Current Treatment Landscape
Traditional treatments for hyperthyroidism aim to normalize thyroid hormone levels and alleviate symptoms. Antithyroid medications such as methimazole and propylthiouracil (PTU) inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis, while radioactive iodine therapy selectively destroys overactive thyroid cells. In cases where these interventions are ineffective or contraindicated, surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be necessary.
Emerging Research and Therapies
- Targeted Molecular Therapies: Recent research has focused on developing targeted molecular therapies that specifically inhibit pathways involved in thyroid hormone production and secretion. For example, small molecule inhibitors targeting the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR) have shown promise in reducing thyroid hormone levels and symptom severity in patients with Graves’ disease, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
- Immunomodulatory Agents: Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the production of autoantibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland. Immunomodulatory agents, such as rituximab and other biological therapies, aim to modulate the immune response and reduce antibody-mediated thyroid stimulation. Clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of these agents in Graves’ disease management are underway, with preliminary results showing encouraging outcomes.
- Thyroid Hormone Receptor Antagonists: Another emerging approach involves the development of thyroid hormone receptor antagonists, which competitively block the binding of thyroid hormones to their receptors. These agents offer a novel mechanism for reducing the effects of excess thyroid hormone activity without directly affecting hormone synthesis or secretion. Preliminary studies suggest that thyroid hormone receptor antagonists may be effective in controlling hyperthyroidism symptoms while minimizing adverse effects.
- Gene Therapy: Gene therapy holds promise as a potential long-term solution for hyperthyroidism by targeting the underlying genetic abnormalities responsible for thyroid dysfunction. Researchers are exploring gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, to correct genetic mutations associated with hyperthyroidism and restore normal thyroid function. While still in the experimental stages, gene therapy offers a potentially curative approach for individuals with hereditary forms of hyperthyroidism.
- Nutraceuticals and Herbal Therapies: Some studies have investigated the use of nutraceuticals and herbal therapies as adjunctive treatments for hyperthyroidism. Compounds such as L-carnitine, selenium, and certain herbal extracts have been proposed to modulate thyroid function and reduce symptoms. While evidence supporting their efficacy is limited, these complementary approaches warrant further investigation as potential adjuvants to conventional treatments.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising developments in hyperthyroidism management, several challenges remain. These include the need for rigorous clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of emerging therapies, as well as considerations regarding patient selection, individualized treatment approaches, and long-term outcomes. Additionally, healthcare providers must remain vigilant in monitoring patients for potential adverse effects and treatment complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, emerging research and therapies offer hope for improved outcomes in hyperthyroidism management. From targeted molecular therapies to gene editing techniques, innovative approaches are reshaping the treatment landscape and providing new options for individuals with hyperthyroidism. However, continued research, collaboration, and clinical validation are essential to translate these advancements into safe and effective treatments that benefit patients worldwide.