Diagnosis And Treatment Of Thyroiditis: What You Need To Know
Thyroiditis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland, can significantly impact one’s health and well-being. Understanding its diagnosis and treatment is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of diagnosing thyroiditis and explore various treatment options available to patients.
Understanding Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck. This gland plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall body function. Thyroiditis can be caused by a variety of factors, including autoimmune disorders, viral infections, radiation therapy, and certain medications.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing thyroiditis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, palpitations, and changes in mood or cognition may prompt further investigation. Blood tests, including thyroid function tests (TFTs) and thyroid antibody tests, are commonly used to assess thyroid hormone levels and detect autoimmune involvement.
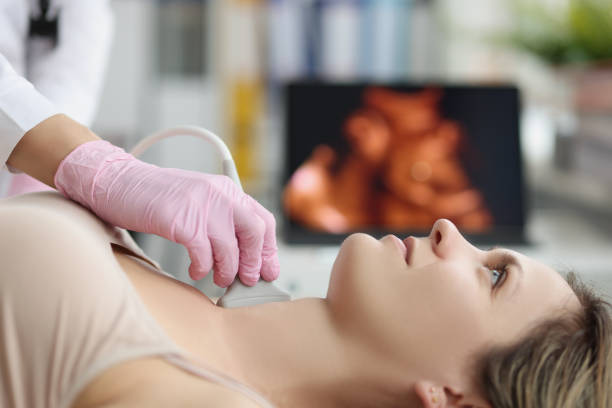
Additionally, imaging studies such as ultrasound may be performed to evaluate the size and appearance of the thyroid gland. Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) may be recommended if nodules or suspicious findings are present, to rule out thyroid cancer.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for thyroiditis depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors. In many cases, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and restoring thyroid hormone balance.
1. Observation:
In mild cases of thyroiditis, particularly those caused by viral infections or temporary inflammation, observation, and supportive care may be sufficient. This may include rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers for discomfort.
2. Medications:
a. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation associated with thyroiditis.
b. Corticosteroids: In cases of severe inflammation or autoimmune thyroiditis, corticosteroids may be prescribed to suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation.
c. Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy: For patients with hypothyroidism resulting from thyroiditis, thyroid hormone replacement therapy (e.g., levothyroxine) may be necessary to restore normal thyroid function.
3. Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Therapy:
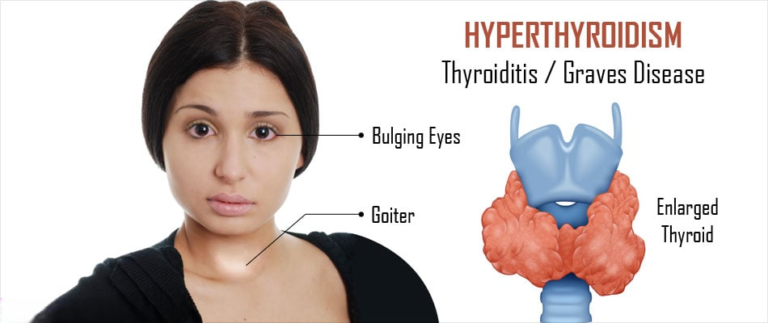
RAI therapy may be considered for patients with hyperthyroidism or Graves’ disease, conditions that can be associated with thyroiditis. RAI therapy involves the administration of radioactive iodine, which selectively destroys thyroid tissue and helps normalize thyroid hormone levels.
4. Surgery:
In rare cases where thyroiditis causes significant enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter) or if nodules are suspicious for cancer, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be recommended.
5. Lifestyle Modifications:
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in managing thyroiditis. This may include maintaining a healthy diet rich in iodine and selenium, managing stress levels, getting regular exercise, and avoiding smoking.
6. Regular Monitoring:
Regardless of the chosen treatment approach, regular monitoring of thyroid function is essential to ensure optimal management of thyroiditis. This may involve periodic blood tests to assess thyroid hormone levels and thyroid antibody titers, as well as imaging studies to monitor changes in thyroid gland size and appearance.
Conclusion
Thyroiditis is a complex condition that requires careful diagnosis and tailored treatment to effectively manage symptoms and optimize long-term health outcomes. By understanding the various diagnostic methods and treatment options available, patients can work closely with their healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans that address their unique needs and preferences. Through ongoing monitoring and proactive management, individuals with thyroiditis can achieve improved quality of life and overall well-being.