Complications Of Untreated Hyperthyroidism: What You Need To Know
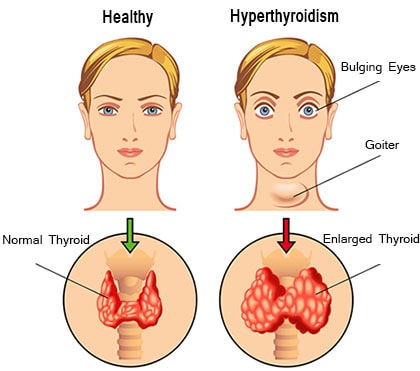
Hyperthyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces an excess amount of thyroid hormones, leading to a hypermetabolic state. This condition can significantly affect various systems in the body if left untreated, resulting in a range of complications. Understanding these potential complications is crucial for recognizing the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment.
Cardiovascular Complications
One of the most serious consequences of untreated hyperthyroidism is its effect on the cardiovascular system. The excess thyroid hormones increase the heart rate and force of contraction, leading to several heart-related issues:
- Atrial Fibrillation: Hyperthyroidism can cause atrial fibrillation, an irregular and often rapid heart rate that can lead to blood clots, stroke, and heart failure. The heart’s upper chambers (atria) beat chaotically and irregularly, out of coordination with the lower chambers (ventricles).
- Heart Failure: Over time, the heart can become unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, leading to heart failure. This occurs because the heart has to work harder to keep up with the increased metabolic demands caused by excessive thyroid hormones.
- Hypertension: The elevated levels of thyroid hormones can cause high blood pressure, which in turn can lead to other serious health issues, including an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Osteoporosis and Bone Health
Untreated hyperthyroidism can also lead to osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened and brittle bones. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in the balance of bone formation and resorption. Excess thyroid hormones accelerate bone turnover, leading to a net loss of bone density. This makes bones more susceptible to fractures, even with minor falls or injuries.
Thyroid Storm
One of the most acute and life-threatening complications of untreated hyperthyroidism is a thyroid storm. This is a sudden and severe exacerbation of hyperthyroidism symptoms, often triggered by stress, infection, surgery, or trauma. Symptoms of a thyroid storm include a high fever, rapid heartbeat, vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, and confusion. Without immediate medical intervention, a thyroid storm can be fatal.
Muscle Weakness and Wasting
Hyperthyroidism can lead to muscle weakness and wasting, a condition known as thyrotoxic myopathy. Patients may experience difficulty in performing routine activities, such as climbing stairs or lifting objects. The muscle weakness typically affects the proximal muscles, those closer to the trunk of the body, such as the thighs and shoulders.
Eye Problems
Graves’ disease, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, can lead to eye complications collectively known as thyroid eye disease (TED) or Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Symptoms can range from mild dryness and irritation to more severe issues such as:
- Exophthalmos: This condition is characterized by bulging eyes, which can cause discomfort, dryness, and vision problems. In severe cases, it can lead to optic nerve compression and vision loss.
- Double Vision: The inflammation and swelling of the eye muscles can lead to misalignment of the eyes, causing double vision (diplopia).
- Eye Pain and Redness: The eyes may become red and painful due to inflammation of the tissues around the eyes.
Psychological and Emotional Effects
Hyperthyroidism can significantly impact mental health, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, mood swings, and depression. The high levels of thyroid hormones can affect the brain’s neurotransmitter balance, contributing to these psychological issues. Additionally, the physical symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as rapid heartbeat and tremors, can exacerbate anxiety and stress.
Reproductive Health Issues
Untreated hyperthyroidism can affect reproductive health in both men and women. In women, it can cause menstrual irregularities, such as lighter or less frequent periods. Severe cases can lead to amenorrhea, the absence of menstruation, which can affect fertility. In men, hyperthyroidism can lead to reduced sperm count and motility, affecting fertility.
Skin Problems
Hyperthyroidism can cause skin changes, including thinning of the skin, increased sweating, and the development of a rash known as pretibial myxedema. This rash is characterized by thickening and reddening of the skin, usually on the shins and feet.
Metabolic Complications
The hypermetabolic state caused by excess thyroid hormones can lead to significant weight loss despite an increased appetite. This can result in nutritional deficiencies and muscle wasting. Additionally, hyperthyroidism can increase the risk of developing diabetes due to its effects on glucose metabolism.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Untreated hyperthyroidism can cause a variety of gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea, increased bowel movements, and abdominal pain. These symptoms result from the increased motility of the gastrointestinal tract caused by excess thyroid hormones.
Conclusion
The complications of untreated hyperthyroidism are extensive and can affect nearly every system in the body. Cardiovascular issues, osteoporosis, thyroid storm, muscle weakness, eye problems, psychological effects, reproductive health issues, skin problems, metabolic complications, and gastrointestinal issues highlight the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment. If you suspect you have hyperthyroidism, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Effective management of hyperthyroidism can prevent these complications and improve overall quality of life. Regular monitoring and appropriate treatment, including medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery, can help control thyroid hormone levels and mitigate the risks associated with this condition.