



At Dr Taneja’s Thyroid Clinic, Dr Vijay Taneja and his staff strive to provide patients with the best and most holistic treatment. Consultation is provided after an in-depth review of the patient’s history, symptoms and lifestyle.
Dr. Vijay Taneja with more than 30 years experience in treating only thyroid disorders provides the best & holistic treatment to patients.
Clinic offers specialised testing, such as Free Thyroid profile & other tests for accurate and early diagnosis.
Dr Taneja at Dr. Taneja’s Thyroid clinic provides individualized treatment options tailored to each patient’s specific condition and needs.
The clinic has access to the latest therapies and treatment options specifically designed for thyroid conditions like radioiodine treatment for cure of certain thyroid diseases.
Thyroid health often requires long-term management, and the clinic provides regular monitoring and support to adjust treatment as needed.
Dr. Taneja at clinic offers a holistic approach, addressing related lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and mental health to support overall wellness.
At Dr. Taneja’s Thyroid Clinic, Dr Vijay Taneja and his team of staff strive to provide best and holistic treatment to patients.
Diagnostic services are also provided for various investigations like FreeT3, FreeT4 and TSH, Thyroid Antibodies etc.
Radio-iodine therapy for permanent treatment of hyperthyroidism is provided
Medicines prescribed by Dr. Vijay Taneja are dispensed at Clinic pharmacy at 20% discount on MRP for the convenience of the patients.
Dr. Vijay Taneja has over 30 years of experience treating thyroid disorders at many of Delhi’s top hospitals and his clinic in Moti Nagar. He has great expertise in managing complex thyroid disorders as well as working with the latest technologies in Nuclear Medicine & Thyroid to provide the best care for patients. He is among the few doctors in Delhi with vast experience in dealing with radio-iodine therapy & other radioisotopes for imaging and curing certain thyroid disorders.

Happy Patient +
Years of Experience +

Sincere & ethical doctor who cares for his patients. He has helped me a lot in managing my disease. I had a nodule in my thyroid & was advised surgery. However Dr. Taneja after getting it evaluated confirmed that it was not cancerous & managed it with medicines. The nodule has now practically vanished Thanks
Excellent doctor, extremely competent and takes pain to explain everything regarding the disease process, medicines and lifestyle changes required.
Exceptional doctor My sister's thyroid levels were very high and weren't coming down. We went to three doctors but the results were not showing..We met Dr Taneja and within one month the TSH levels came down and withing normal range...Really Happy the way he treats..
Dr. Vijay Taneja at Dr. Taneja's Thyroid Clinic provides personalized care rarely seen in doctors now a days. In plush but relaxed surroundings I was given very good treatment and lifestyle advise by Dr. Taneja which helped me in feeling better after a long time. I am now practically pain free and all my symptoms from hypothyroidism have vanished. I have even lost some weight which was stuck for ages. Thanks once again Dr. Taneja for excellent management of my disease.
Dr Vijay Taneja is a very good doctor... I will definitely recommend him for thyroid disorders I got diagnosed with hypothyroidism 5 years ago and have been getting treatment from him since then. He is very good. He explained things in a way that I could understand and did not ask me to get lots of tests but actually listened to what symptoms I was having and gave me treatment according to that. He also talked to me about my diet and exercise and did not give me some ridiculously long list of things that I could not eat like some other doctors did, but rather spoke very practically and gave me advice that I could actually follow... So if ur looking for a genuine doctor who actually knows what he is doing go to Dr Taneja
Remarkable services, genuine and apt consultation and lifestyle advice. Highly experienced doctor. Commendable overall experience
My disease was explained in detail and good lifestyle advice was given which helped me get well.
Doctor is very competent with more than thirty years experience in treating thyroid patients. I had major issues with my thyroid for last many years and I am feeling great after his treatment. Highly recommended.
Compassionate and professionally competent doctor. He is very patient friendly and has in depth knowledge of his subject. Best doctor in Delhi for thyroid diseases.
You are not only a good Doctor, but also a simple, sober, good Human being, with smiling face. And always Approachable
Hypothyroidism can develop due to a wide variety of factors, ranging from autoimmune disorders and iodine deficiency to ...
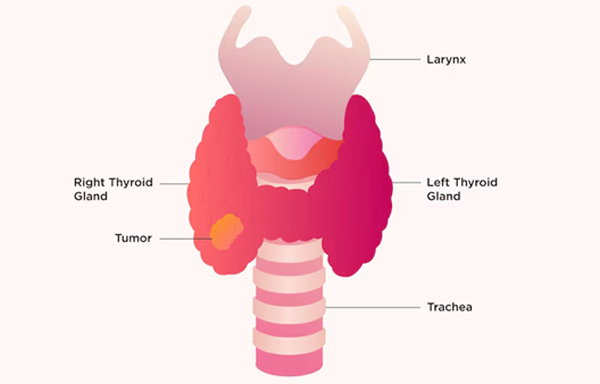
Thyroid tumors can arise due to multiple factors, including genetic predisposition, exposure to radiation, autoimmune co...
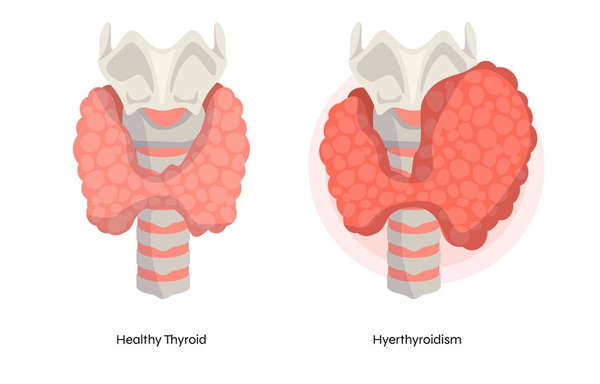
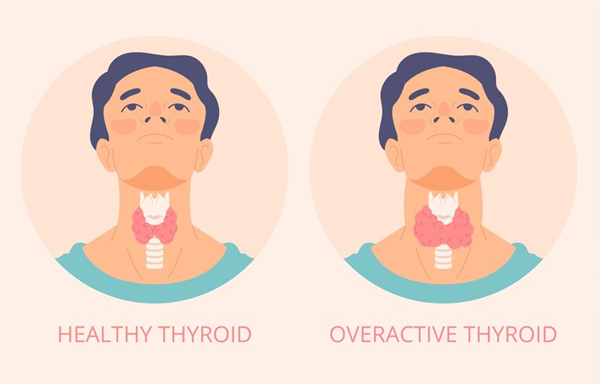
Hyperthyroidism arises due to various medical conditions, including Graves’ disease, toxic multinodular goiter, or...