Thyroid Troubles: A Closer Look At Simple Goitre Symptoms
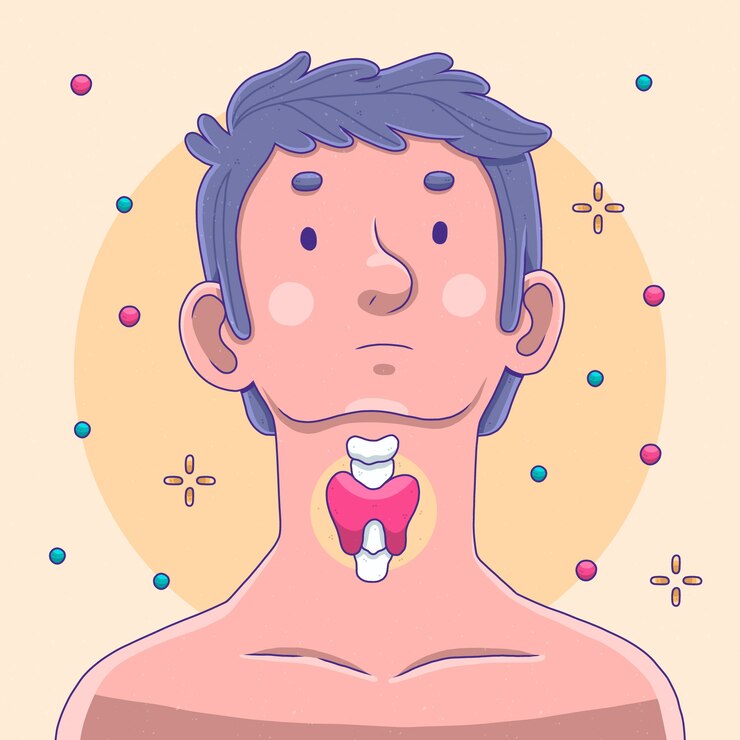
The thyroid gland, a small, butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. When the thyroid encounters issues, it can lead to a range of disorders, one of which is simple goitre. In this article, we will delve into the details of simple goitre symptoms, understand the warning signs, and explore the importance of early detection and management.
Understanding the Thyroid and Simple Goitre
Before diving into the symptoms, let’s take a moment to understand the thyroid gland’s role in the body. The thyroid produces hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which influence metabolism, growth, and energy levels. The secretion of these hormones is tightly regulated by the pituitary gland through thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
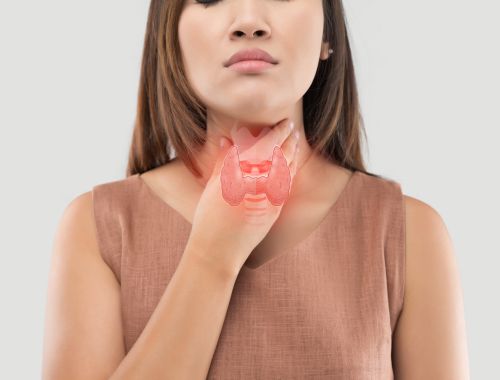
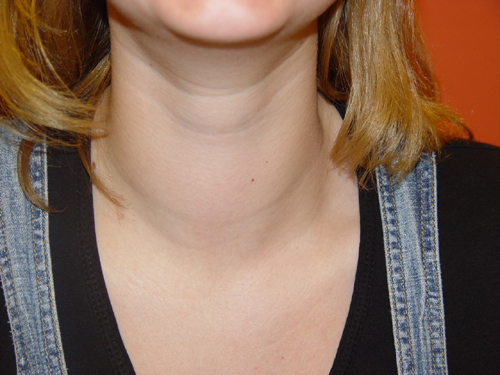
Simple goitre, also known as non-toxic goitre or colloid goitre, is a condition characterized by the enlargement of the thyroid gland. This enlargement is often visible as a swelling in the neck and can result from various factors, including iodine deficiency, hormonal imbalances, or genetic predisposition.
Common Symptoms of Simple Goitre
Neck Swelling:
The most noticeable symptom of simple goitre is the swelling of the thyroid gland in the neck. This enlargement can range from a small, barely noticeable lump to a visibly enlarged mass. The swelling is usually painless and may develop gradually over time.
Difficulty Swallowing:
As the thyroid gland enlarges, it can exert pressure on the surrounding structures, including the esophagus. This pressure may lead to difficulty swallowing, a condition known as dysphagia. Individuals with simple goitre may experience a sensation of a lump in the throat or discomfort while swallowing.
Hoarseness or Voice Changes:
The enlarged thyroid gland can also compress the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which controls the vocal cords. This compression may result in hoarseness or changes in the voice. Persistent hoarseness should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Breathing Difficulties:
In severe cases, an enlarged thyroid may affect the trachea, causing breathing difficulties. Individuals with simple goitre may experience shortness of breath, especially when lying down or during physical activity.
Irritation and Coughing:
The pressure on the trachea and surrounding structures can lead to irritation and a persistent cough. This symptom is often a consequence of the thyroid gland’s physical impact on the respiratory system.
Visible Neck Veins:
In some cases, the enlargement of the thyroid gland can lead to the visibility of veins on the neck’s surface. This occurs due to increased blood flow in the region as the body attempts to supply more nutrients and oxygen to the enlarged thyroid.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of simple goitre is crucial for effective management and preventing complications. While the condition itself is generally benign, an enlarged thyroid can be an indication of an underlying thyroid disorder or other health issues.
Thyroid Function Testing:
A comprehensive evaluation of thyroid function, including blood tests measuring TSH, T4, and T3 levels, helps determine if the thyroid is functioning within normal parameters. Abnormal thyroid hormone levels may indicate an underlying thyroid disorder contributing to the goitre.
Imaging Studies:
Ultrasound imaging can provide a detailed view of the thyroid gland, helping healthcare professionals assess its size, structure, and any nodules present. This diagnostic tool aids in determining the cause of the enlargement and guiding appropriate treatment.
Iodine Levels:
Since iodine deficiency is a common cause of simple goitre, measuring iodine levels in the body can help identify and address this specific cause. Iodine supplementation may be recommended to correct deficiencies.
Treatment Options
The approach to treating simple goitre depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. Here are common treatment options:
Iodine Supplementation:
In cases where iodine deficiency is identified, supplementation may be prescribed to address the root cause. Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, and ensuring an adequate supply can help shrink the goitre.
Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy:
If thyroid function tests reveal hormonal imbalances, thyroid hormone replacement therapy may be recommended. This involves taking synthetic thyroid hormones to restore normal hormone levels and reduce the size of the goitre.
Monitoring and Observation:
In mild cases with no significant symptoms, healthcare professionals may choose to monitor the goitre without immediate intervention. Regular check-ups and thyroid function tests ensure that any changes can be addressed promptly.
Surgery:
In cases where the goitre causes severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or swallowing, or if there’s a suspicion of thyroid cancer, surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be recommended.
Conclusion
Simple goitre, though often benign, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life if left untreated. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention, and undergoing necessary diagnostic tests are essential steps in managing this thyroid disorder. Whether through iodine supplementation, hormone replacement therapy, or surgery, the goal is to restore thyroid function, alleviate symptoms, and prevent potential complications. As with any health concern, consulting with healthcare professionals ensures a tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment, promoting optimal thyroid health and overall well-being.