Understanding and Managing Thyroiditis: What You Need to Know
Discover the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for thyroiditis in this informative blog. Gain a better understanding of this condition and how to manage it for optimal health.
Thyroiditis, an inflammation of the thyroid gland, is a condition that can significantly impact the proper functioning of this crucial endocrine organ. The thyroid plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and various bodily functions. Thyroiditis can manifest in different forms, each with its own set of causes, symptoms, and management strategies. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various types of thyroiditis, delve into their causes, and symptoms, and discuss effective management approaches for individuals grappling with this condition.
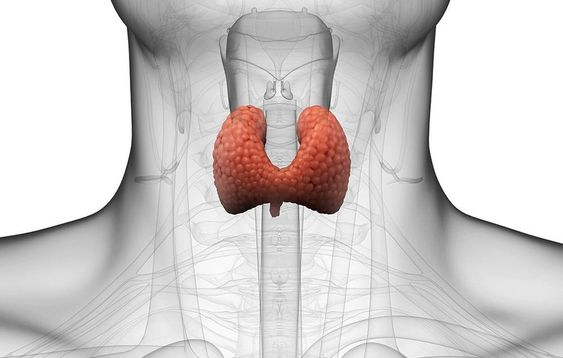
The Thyroid Gland: An Overview
The thyroid gland, located at the base of the neck, produces hormones that play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall bodily functions. The two main hormones produced by the thyroid are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones influence the rate at which cells produce energy and are integral to maintaining a healthy balance in the body.
Types of Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: An autoimmune condition, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. This results in chronic inflammation and can eventually lead to hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid is underactive.
Graves’ Disease: Another autoimmune disorder, Graves’ disease, involves the immune system mistakenly attacking the thyroid, causing it to become overactive. This leads to excessive production of thyroid hormones, a condition known as hyperthyroidism.
Subacute Thyroiditis: The common cause of subacute thyroiditis is a viral infection. It causes inflammation of the thyroid gland, leading to pain and tenderness in the neck. This type of thyroiditis may result in a temporary hyperthyroid phase followed by a hypothyroid phase.
Silent Thyroiditis: Silent thyroiditis is similar to subacute thyroiditis but lacks the characteristic neck pain. It can lead to temporary hyperthyroidism, followed by a hypothyroid phase.
Postpartum Thyroiditis: Some women may experience thyroid inflammation in the postpartum period, typically within the first year after giving birth. This condition can manifest as hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or a combination of both.
Causes of Thyroiditis
Autoimmune Factors: Autoimmune thyroiditis, including Hashimoto’s and Graves’ disease, is primarily caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking the thyroid gland.
Viral Infections: Subacute and silent thyroiditis can be triggered by viral infections. The inflammation is often a result of the body’s immune response to the infection.
Postpartum Changes: Postpartum thyroiditis is believed to be linked to the changes in the immune system that occur after childbirth.
Genetic Predisposition: There may be a genetic predisposition to thyroiditis, especially in cases of autoimmune thyroid disorders.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those occurring during pregnancy or menopause, can contribute to the development of thyroiditis.
Symptoms of Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, muscle aches, and joint pain.
Graves’ Disease: Symptoms of Graves’ disease may include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, irritability, and difficulty sleeping.
Subacute Thyroiditis: Individuals with subacute thyroiditis may experience neck pain, fever, fatigue, and in some cases, symptoms of hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism.
Silent Thyroiditis: Similar to subacute thyroiditis, silent thyroiditis can lead to hyperthyroid symptoms followed by a hypothyroid phase, but without the characteristic neck pain.
Postpartum Thyroiditis: Symptoms may vary but can include fatigue, mood swings, weight changes, and changes in menstrual patterns.
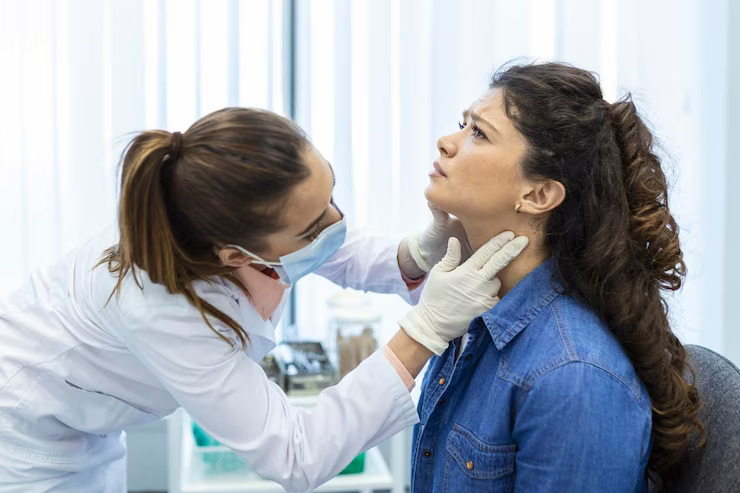
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosing thyroiditis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, and sometimes imaging studies. Blood tests typically measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and antibodies associated with autoimmune thyroiditis. Imaging studies such as ultrasound may be used to visualize the thyroid gland and assess its size and condition.
Management and Treatment
Medication: Depending on the type of thyroiditis and the symptoms presented, medications may be prescribed. Levothyroxine is commonly used for hypothyroidism, while medications like methimazole or propylthiouracil may be prescribed to manage hyperthyroidism.
Beta-Blockers: Beta-blockers may be prescribed to manage symptoms such as rapid heartbeat and anxiety in cases of hyperthyroidism.
Pain Management: In cases of subacute thyroiditis where neck pain is prominent, pain management strategies may be employed, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular monitoring of thyroid function is essential to track changes and adjust treatment accordingly. Follow-up visits with healthcare providers help ensure that the chosen management plan is effective and well-tailored to the individual’s needs.
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can contribute to overall thyroid health.
Thyroidectomy: In some cases, especially with severe and persistent thyroid disorders, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be recommended.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing thyroiditis requires a multifaceted approach that considers the specific type of thyroiditis, individual symptoms, and the overall health of the patient. Regular monitoring, effective communication with healthcare providers, and adherence to prescribed treatments are essential components of managing thyroiditis successfully. With timely intervention and proper management, individuals diagnosed with thyroiditis can lead healthy and fulfilling lives, minimizing the impact of this condition on their overall well-being. If you suspect you may have thyroiditis or are experiencing symptoms related to thyroid dysfunction, seeking medical advice promptly is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.